Time:2023-12-27
Following the introduction of Linezolid, the global sales reached 782 million US dollars in 2006 and have continued to grow, peaking at 1.353 billion US dollars in 2015. According to Midnet data, total sales of Linezolid exceeded 1.7 billion yuan across the three major terminal markets in 2021. In China, the primary dosage forms of Linezolid are tablets and injections, both of which are included in the national procurement catalog.
Introduction
Today, we prsent research on oxazolidinone antibiotics, specifically focusing on impurities related to Linezolidin. Previously, we shared a comprehensive analysis of ChemStrong’s Memoirs on the Impurity Code PNU142063 of Linezolid.; interested parties are encouraged to refer back to that information. Currently, domestic linezolid formulations and raw materials have received four registration approval numbers, which include four for formulations and none for raw material approvals.
Linezolid is the pioneering synthetic oxazolidinone antibacterial agent globally, targeting the bacterial ribosomal subunit 50S to inhibit protein synthesis. It received approval from the U.S. FDA in 2000 for treating infections caused by Gram-positive (G+) bacteria, including suspected or confirmed hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), complex skin and soft tissue infections (SSTI), as well as Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) infections.
The Presented 19 Key Impurities of Linezolid
Currently, the QCS official website lists a total of 98 impurities associated with Linezolid (please scan the QR code at the end of this article to access the complete list). In conjunction with relevant registration standards and market feedback, the QCS R&D Center has selected these 19 key impurities for dissemination among researchers. The pertinent product structural information discussed in this paper is illustrated in Figure 1.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 1: list of linezolid impurities that customers focus on
Research Presentation Utilizing Standardized Methodologies for Import Registration
The 19 impurity products introduced in this instance encompass various categories of process impurities, degradation impurities, and others. Among these, 11 impurity products are incorporated into the import registration standard for Linezolid Dry Suspension (Standard No. JX20150196). The QCS R&D Center conducted qualitative characterization research on the 19 impurity products in accordance with the relevant substance methodology outlined in the import registration standard for Linezolid Dry Suspension (Standard No. JX20150196). The chromatographic data from mixed samples is presented in Figure 2.
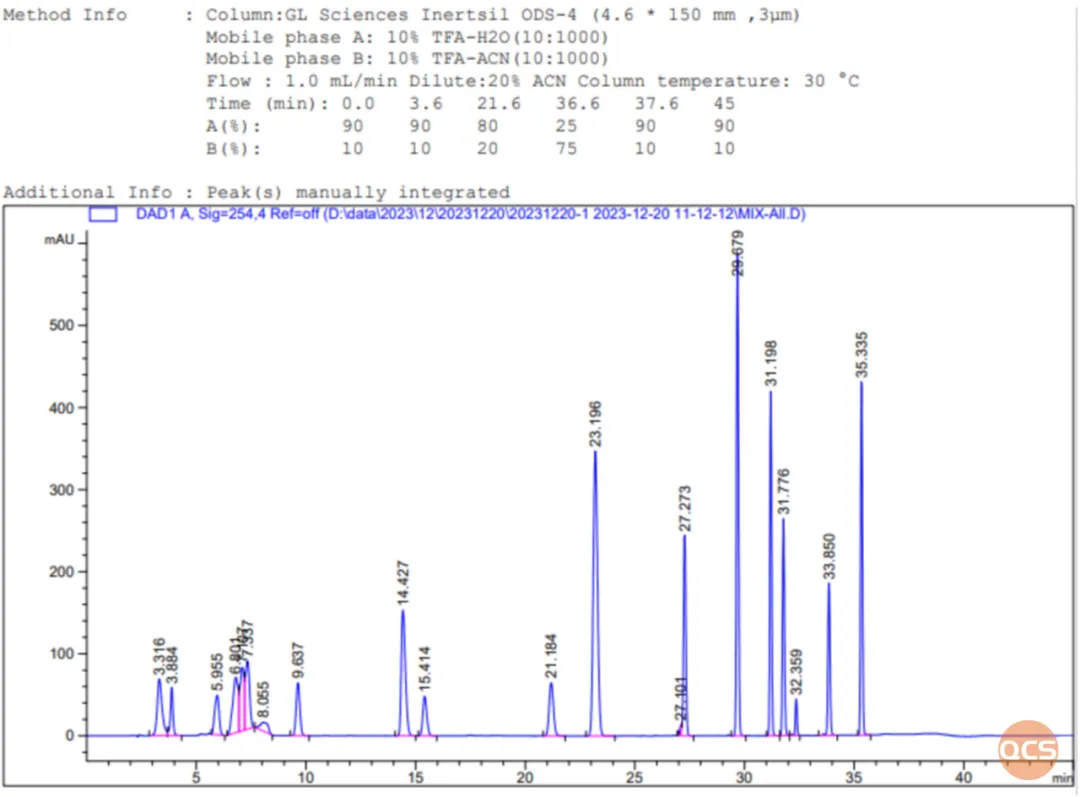
Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 2: comprehensive analytical data summary of impurities associated with Linezolid 19 and the locations of the API
In this study, the QCS R&D Center selected a total of 19 impurity products and APIs for a comprehensive series of investigations, which included 11 standard impurities. Under the current chromatographic conditions, the measured relative retention times of the impurity products aligned with those in the standards, demonstrating consistency with standard data. Furthermore, the chromatographic results for import registration standards were effectively reproduced.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 3: standards for code impurity and validation data in import registration regulations
The registration process, based on the established standards, has led to an expansion of issues related to other impurities at the QCS R&D center. The table below summarizes the findings regarding all 19 impurity types, including RM-L142601, RM-L142605, RM-L142614, RM-L142623, RM-L142638, RM-L142652, RM-L142654, and RM-L241606 as well as RM-L241630—these impurities are not included in the standard.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 4: illustrates the impurity location data along with a comprehensive data summary
Further Evaluation of RM-L142629 (PNU-143797)
The objective of this study is to evaluate 19 products from the QCS Standard Material R&D Center using a standardized chromatographic method. As illustrated in Figure 2, the simultaneous injection of 19 impurities and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) under these chromatographic conditions results in certain impurities co-eluting, which hampers effective separation. For instance, the retention times for raw material components RM-L142600, RM-L142630, and RM-L142623 are approximately 23 minutes. Under mixed injection conditions, these three components elute together (refer to Figure 5 for chromatographic results from independent injections).
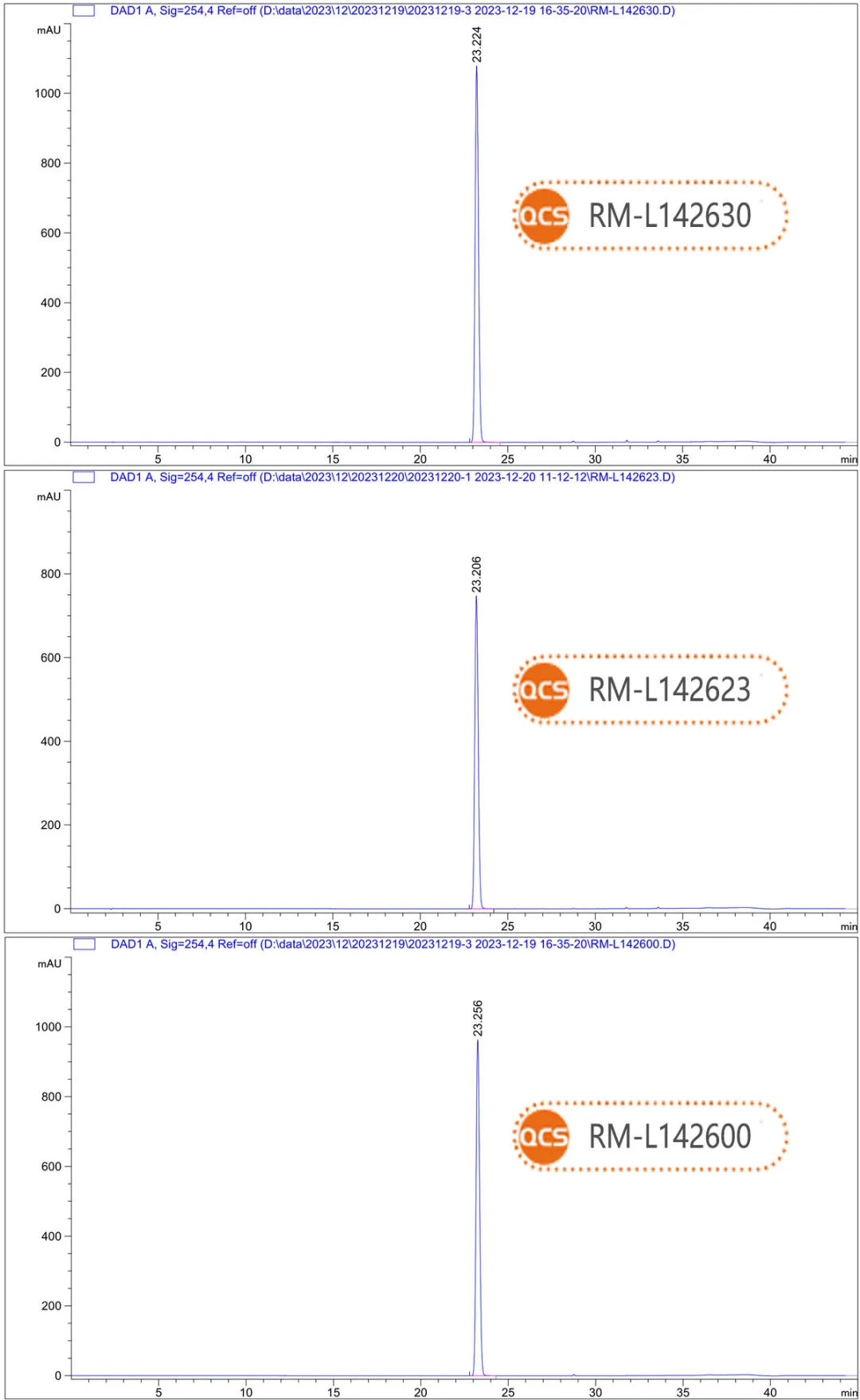
Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center.
Figure 5: illustrates the injection results of raw material components RM-L142600, RM-L142630, and RM-L142623
Upon employing the standard method for import registration to verify RM-L142629 (with the corresponding code in the import standard being PNU-143797), it was observed that the product exhibited complex liquid chromatography results under these conditions, aligning with feedback received from our previous customers.
Based on customer feedback records from the QCS R&D Center, certain clients have reported observing multiple sets of peaks in HPLC analyses under specific chromatographic conditions while utilizing RM-L142629. The observed chromatographic results may stem from discrepancies between the mobile phase and stationary phase. Furthermore, during quality monitoring via hydrogen NMR spectroscopy, no product degradation was detected, which can be attributed to the suitability of the chromatographic conditions.
Through the optimization of chromatographic mobile phases and packing materials, the QCS R&D Center has developed a suitable chromatographic method that yields precise test results (refer to Figure 7 for chromatographic methodologies or consult the COA report). Based on these findings, the QCS R&D Center hypothesizes that under specific analytical conditions, the product may undergo decomposition due to the inherent stability of its shrink ring structure (highlighted in red in Figure 6), leading to complex outcomes. Should you require assistance while utilizing this product, please do not hesitate to reach out to our scientists at the QCS R&D Center.
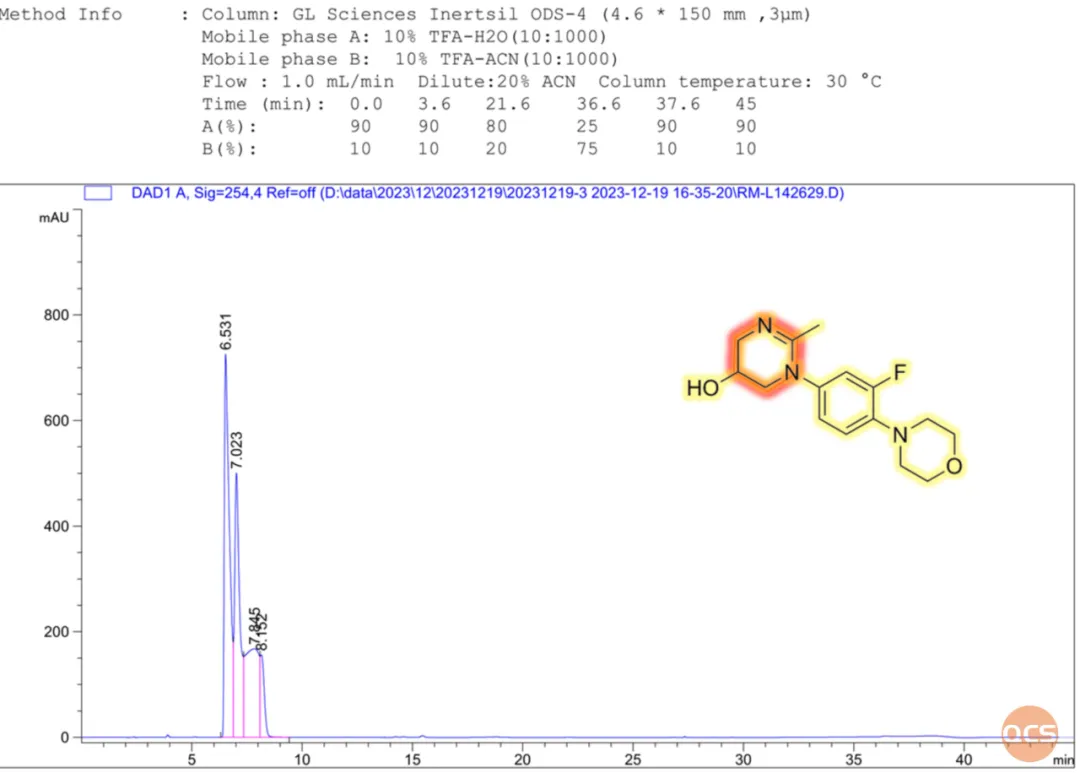
Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 6: HPLC chromatographic analysis results of RM-L142629 according to the import registration standard methodology

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 7: HPLC chromatographic analysis of RM-L142629 utilizing the liquid chromatography method developed in-house by QCS
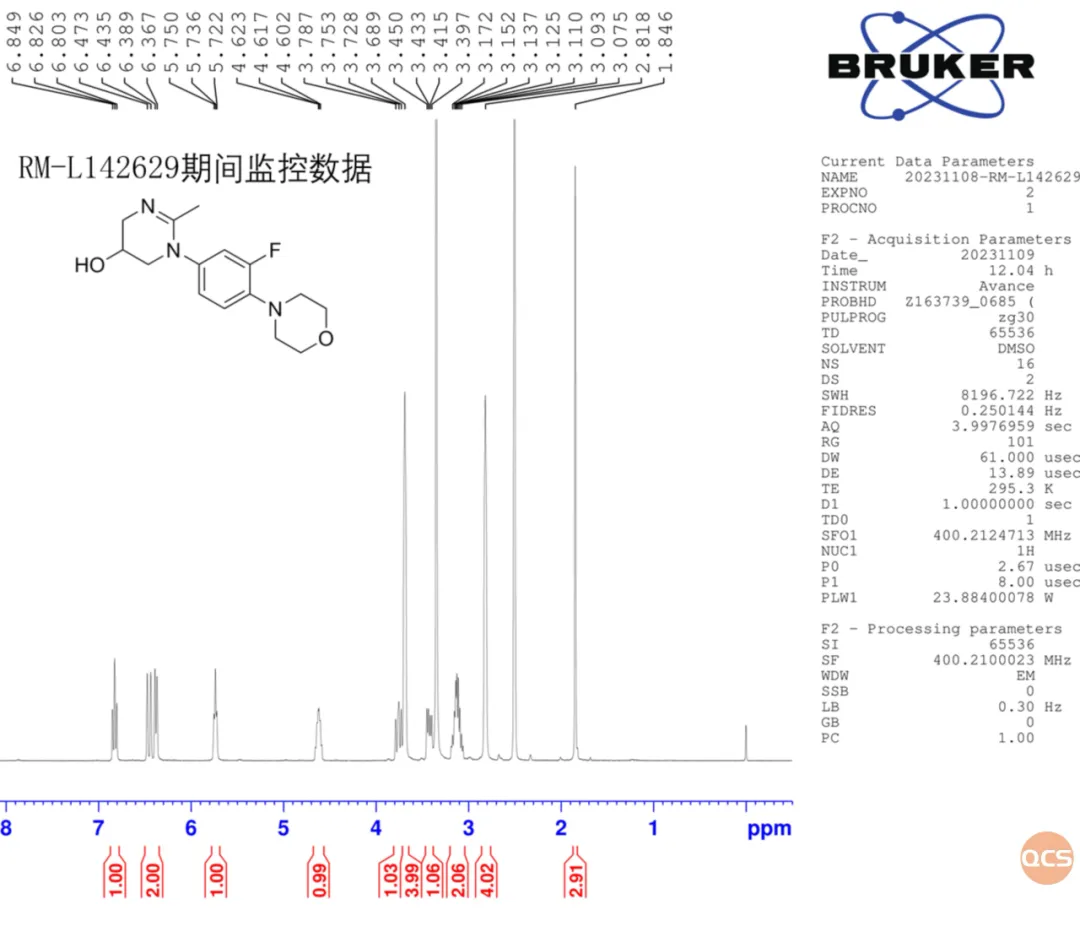
Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 8: HNMR monitoring chart for the RM-L142629 product over a 9-month period
Under the widely adopted import registration standard method, the chromatographic results for RM-L142629 may overlap with those of other impurity products, particularly concerning the retention times of RM-L142607 (designated as PNU140155 in the import standard) and RM-L142629, which were emphasized in the investigation of linezolid sodium chloride injection.
Consequently, the researchers at our center acquired samples of RM-L142607 and RM-L122605 (PNU142063), which have garnered significant attention from numerous researchers, for further experimental validation. In this study, these two samples will be combined with the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) for injection, and chromatographic results will be collected for confirmation. The chromatographic analysis (FIG. 9) demonstrates that the two impurities can be effectively separated from the API under the chromatographic conditions specified in the relevant substance inspection criteria of the import registration standard (Standard No. JX20150196). The separation chromatogram is illustrated in FIG. 9.
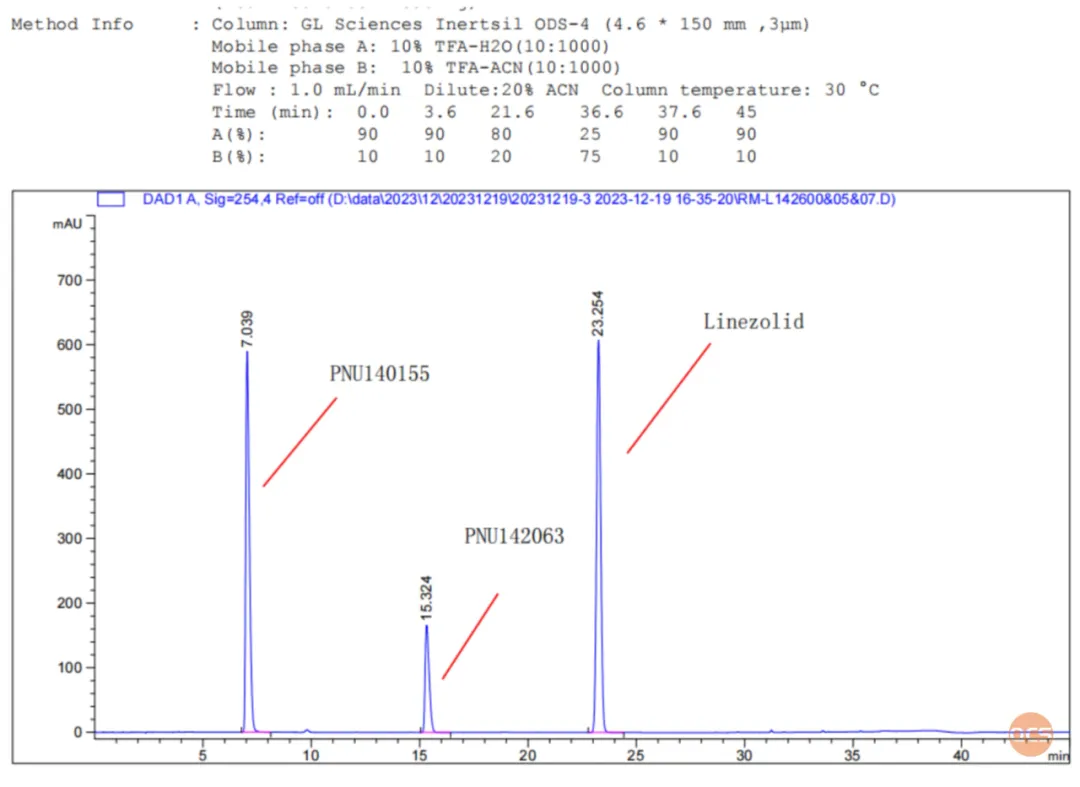
Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 9: injection patterns of mixtures RM-L142600, RM-L142605, and RM-L142607
Summary
To enhance the quality of chromatographic reference information, the QCS Standard Material Research and Development Center conducted a rigorous individual sample injection test on the 19 selected impurity products. By integrating the results from both single sample tests and mixed sample analyses, we aim to provide a more comprehensive reference for linezolid impurity research. Due to space limitations, only a portion of the mixed sample test data is presented in this paper. For further details, please contact our business department to obtain the complete chromatographic results for each impurity product.
Please long-press the QR code to access a list of all impurities!


Following the introduction of Linezolid, the global sales reached 782 million US dollars in 2006 and have continued to grow, peaking at 1.353 billion US dollars in 2015. According to Midnet data, total sales of Linezolid exceeded 1.7 billion yuan across the three major terminal markets in 2021. In China, the primary dosage forms of Linezolid are tablets and injections, both of which are included in the national procurement catalog.
Introduction
Today, we prsent research on oxazolidinone antibiotics, specifically focusing on impurities related to Linezolidin. Previously, we shared a comprehensive analysis of ChemStrong’s Memoirs on the Impurity Code PNU142063 of Linezolid.; interested parties are encouraged to refer back to that information. Currently, domestic linezolid formulations and raw materials have received four registration approval numbers, which include four for formulations and none for raw material approvals.
Linezolid is the pioneering synthetic oxazolidinone antibacterial agent globally, targeting the bacterial ribosomal subunit 50S to inhibit protein synthesis. It received approval from the U.S. FDA in 2000 for treating infections caused by Gram-positive (G+) bacteria, including suspected or confirmed hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), complex skin and soft tissue infections (SSTI), as well as Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) infections.
The Presented 19 Key Impurities of Linezolid
Currently, the QCS official website lists a total of 98 impurities associated with Linezolid (please scan the QR code at the end of this article to access the complete list). In conjunction with relevant registration standards and market feedback, the QCS R&D Center has selected these 19 key impurities for dissemination among researchers. The pertinent product structural information discussed in this paper is illustrated in Figure 1.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 1: list of linezolid impurities that customers focus on
Research Presentation Utilizing Standardized Methodologies for Import Registration
The 19 impurity products introduced in this instance encompass various categories of process impurities, degradation impurities, and others. Among these, 11 impurity products are incorporated into the import registration standard for Linezolid Dry Suspension (Standard No. JX20150196). The QCS R&D Center conducted qualitative characterization research on the 19 impurity products in accordance with the relevant substance methodology outlined in the import registration standard for Linezolid Dry Suspension (Standard No. JX20150196). The chromatographic data from mixed samples is presented in Figure 2.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 2: comprehensive analytical data summary of impurities associated with Linezolid 19 and the locations of the API
In this study, the QCS R&D Center selected a total of 19 impurity products and APIs for a comprehensive series of investigations, which included 11 standard impurities. Under the current chromatographic conditions, the measured relative retention times of the impurity products aligned with those in the standards, demonstrating consistency with standard data. Furthermore, the chromatographic results for import registration standards were effectively reproduced.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 3: standards for code impurity and validation data in import registration regulations
The registration process, based on the established standards, has led to an expansion of issues related to other impurities at the QCS R&D center. The table below summarizes the findings regarding all 19 impurity types, including RM-L142601, RM-L142605, RM-L142614, RM-L142623, RM-L142638, RM-L142652, RM-L142654, and RM-L241606 as well as RM-L241630—these impurities are not included in the standard.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 4: illustrates the impurity location data along with a comprehensive data summary
Further Evaluation of RM-L142629 (PNU-143797)
The objective of this study is to evaluate 19 products from the QCS Standard Material R&D Center using a standardized chromatographic method. As illustrated in Figure 2, the simultaneous injection of 19 impurities and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) under these chromatographic conditions results in certain impurities co-eluting, which hampers effective separation. For instance, the retention times for raw material components RM-L142600, RM-L142630, and RM-L142623 are approximately 23 minutes. Under mixed injection conditions, these three components elute together (refer to Figure 5 for chromatographic results from independent injections).

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center.
Figure 5: illustrates the injection results of raw material components RM-L142600, RM-L142630, and RM-L142623
Upon employing the standard method for import registration to verify RM-L142629 (with the corresponding code in the import standard being PNU-143797), it was observed that the product exhibited complex liquid chromatography results under these conditions, aligning with feedback received from our previous customers.
Based on customer feedback records from the QCS R&D Center, certain clients have reported observing multiple sets of peaks in HPLC analyses under specific chromatographic conditions while utilizing RM-L142629. The observed chromatographic results may stem from discrepancies between the mobile phase and stationary phase. Furthermore, during quality monitoring via hydrogen NMR spectroscopy, no product degradation was detected, which can be attributed to the suitability of the chromatographic conditions.
Through the optimization of chromatographic mobile phases and packing materials, the QCS R&D Center has developed a suitable chromatographic method that yields precise test results (refer to Figure 7 for chromatographic methodologies or consult the COA report). Based on these findings, the QCS R&D Center hypothesizes that under specific analytical conditions, the product may undergo decomposition due to the inherent stability of its shrink ring structure (highlighted in red in Figure 6), leading to complex outcomes. Should you require assistance while utilizing this product, please do not hesitate to reach out to our scientists at the QCS R&D Center.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 6: HPLC chromatographic analysis results of RM-L142629 according to the import registration standard methodology

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 7: HPLC chromatographic analysis of RM-L142629 utilizing the liquid chromatography method developed in-house by QCS

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 8: HNMR monitoring chart for the RM-L142629 product over a 9-month period
Under the widely adopted import registration standard method, the chromatographic results for RM-L142629 may overlap with those of other impurity products, particularly concerning the retention times of RM-L142607 (designated as PNU140155 in the import standard) and RM-L142629, which were emphasized in the investigation of linezolid sodium chloride injection.
Consequently, the researchers at our center acquired samples of RM-L142607 and RM-L122605 (PNU142063), which have garnered significant attention from numerous researchers, for further experimental validation. In this study, these two samples will be combined with the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) for injection, and chromatographic results will be collected for confirmation. The chromatographic analysis (FIG. 9) demonstrates that the two impurities can be effectively separated from the API under the chromatographic conditions specified in the relevant substance inspection criteria of the import registration standard (Standard No. JX20150196). The separation chromatogram is illustrated in FIG. 9.

Data Source: QCS Standard Materials Research and Development Center
Figure 9: injection patterns of mixtures RM-L142600, RM-L142605, and RM-L142607
Summary
To enhance the quality of chromatographic reference information, the QCS Standard Material Research and Development Center conducted a rigorous individual sample injection test on the 19 selected impurity products. By integrating the results from both single sample tests and mixed sample analyses, we aim to provide a more comprehensive reference for linezolid impurity research. Due to space limitations, only a portion of the mixed sample test data is presented in this paper. For further details, please contact our business department to obtain the complete chromatographic results for each impurity product.
Please long-press the QR code to access a list of all impurities!


Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号