Time:2023-07-13
Introduction: In this section, we present a challenging concept for the synthesis of an impurity associated with the brain metabolic activator citicoline—specifically, UDPC.
Citicoline serves as a crucial brain metabolic activator and is a derivative of nucleic acids, functioning as a key coenzyme in the synthesis of ovophosphorate. It facilitates cerebral cell respiration, enhances cognitive function, augments the activity of the ascending reticular activating system to promote alertness, reduces cerebrovascular resistance, and thereby improves cerebral blood circulation. This results in alleviation of cerebral hypoxia and optimization of brain matter metabolism; thus, it plays an essential role in human biofilm construction. Clinically, citicoline is primarily employed to address neurological sequelae resulting from traumatic brain injury and cerebrovascular accidents.
Today, we are pleased to present our innovative strategies for the synthesis of Uridine Diphosphate Choline (UDPC), aimed at addressing several challenges encountered in the synthesis process. Through diligent efforts and ongoing experimental exploration, we have achieved significant breakthroughs.
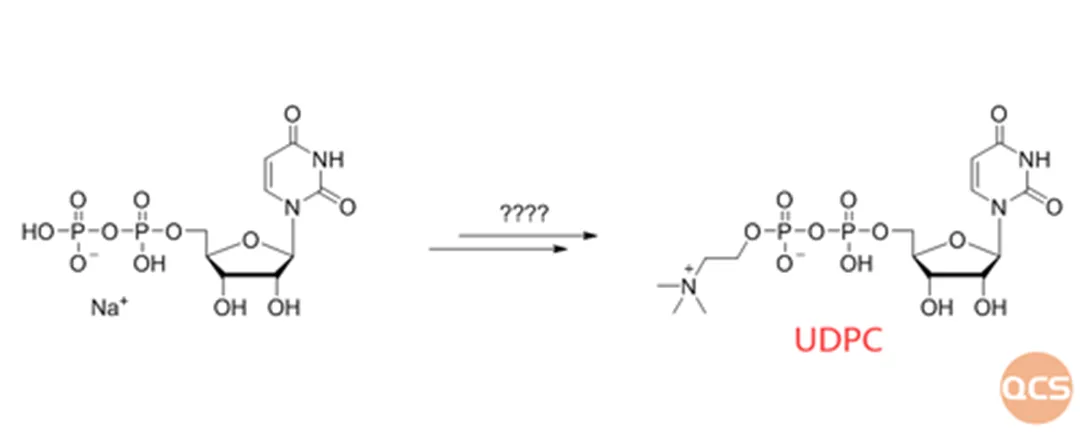
Figure 1: conceptual framework for UDPC Synthesis
As a significant bioactive compound, UDPC exhibits considerable potential for application in the medical field. However, previous synthesis methods have presented challenges such as low yield, complex procedures, and extended time requirements. To address these issues, we have achieved notable advancements through comprehensive research and the implementation of innovative synthetic strategies.
esterification parameters. Following extensive experimentation and comparative analysis, we ultimately identified the best activation reagent, resulting in a substantial enhancement of synthesis yield. This screening process is both intricate and crucial, laying a robust foundation for our subsequent research endeavors. The optimized reaction conditions have increased yield from 18% to 52%. By enhancing the purity of the crude product, subsequent purification operations are rendered significantly simpler.
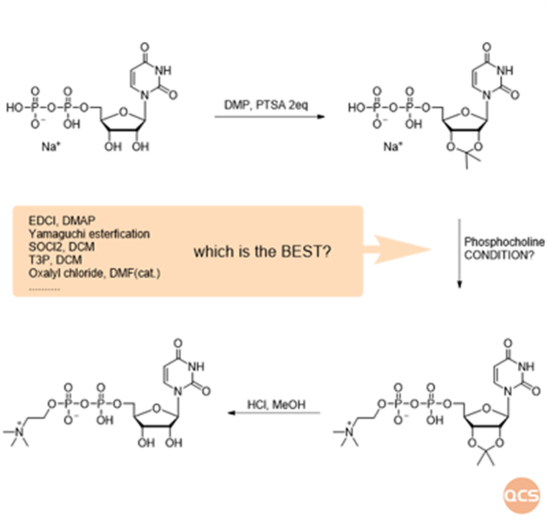
Figure 2: roadmap for UDPC synthesis
By meticulously controlling the reaction time and concentration of hydrochloric methanol, we can effectively eliminate the protective groups on the two hydroxyl moieties, yielding UDPC with approximately 86% purity. While certain fractions exceeding 95% purity can be enriched through reverse preparative chromatography, this method significantly escalates the production costs associated with UDPC products. Ultimately, through iterative exploration of recrystallization protocols, we systematically evaluated 16 solvent systems; notably, a subset of ternary solvent systems successfully addressed this challenge. Through continuous experimentation and optimization, we identified that a critical control factor is the pH level of the product. Only within a specific pH range can efficient purification be achieved swiftly. This finding holds substantial implications for enhancing purity and expediting operational processes.
Through our dedicated efforts and innovative approaches, we have effectively addressed the complex challenges associated with UDPC synthesis and proposed a viable synthesis strategy. This significant breakthrough not only provided a substantial impetus for the development and production of related products but also established a robust foundation for our future research endeavors.
In addition to the structural confirmatory data obtained from nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry, the UDPC was also identified and validated in strict accordance with the USP methodology. The specific findings are as follows: Citicoline contains three primary specific impurities as outlined in the USP standard. Detailed methodologies, impurity profiles, and mixed injection data are presented in Figure 3-5.

Figure 3: chromatographic conditions as per the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) standards
Source: United States Pharmacopeia USP-NF2021
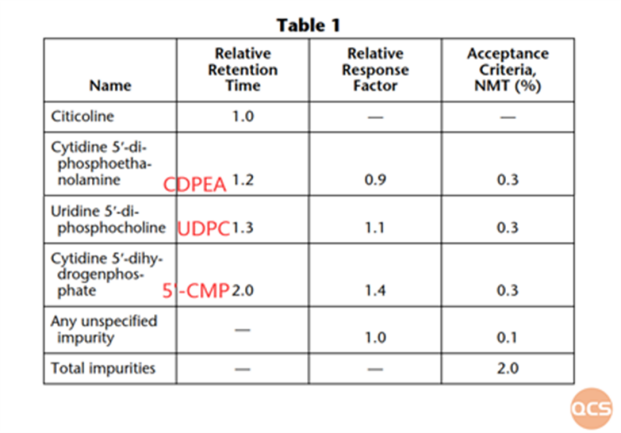
Figure 4: enumeration of specific impurities as outlined in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP)
Source: United States Pharmacopeia USP-NF2021
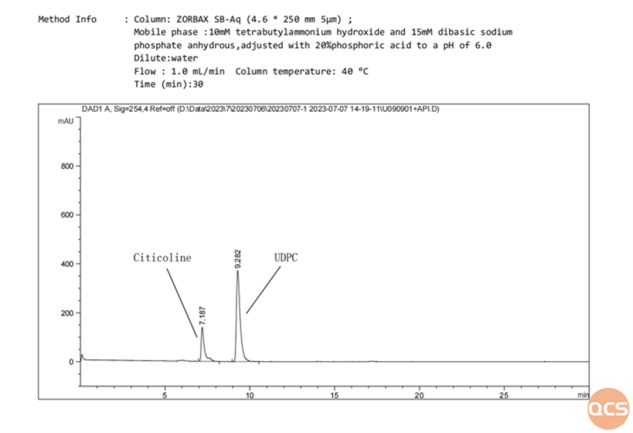
Figure 5: data on mixed UDPC and citicoline injections analyzed according to USP methodology
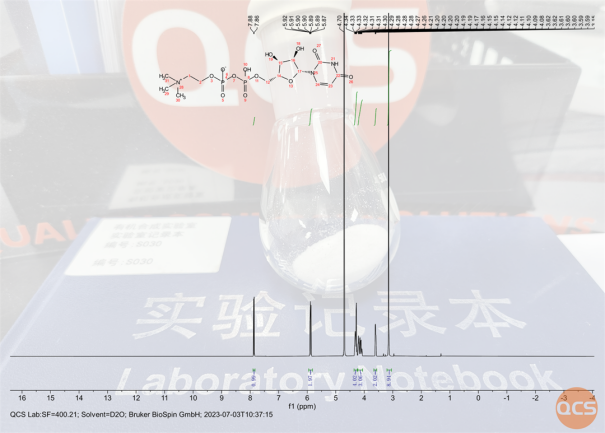
Figure 6: NMR hydrogen spectrum data for this batch of UDPC samples
As illustrated in FIG. 5, the relative retention time (RRT) of UDPC, measured at the QCS Standard Product R&D Center using the USP method, is recorded as 1.28. Furthermore, based on the data presented in FIG. 4, the RRT of UDPC under the USP methodology is noted to be 1.3; thus, the current test results align with established standards.
In conclusion, we would like to express our heartfelt gratitude to every member of the QCS R&D Center for their diligent efforts and unwavering commitment. It is through the collective endeavor and insights of all that we have successfully developed this innovative strategy. We anticipate that our research findings will provide greater inspiration and opportunities for industry development and application. We warmly invite customers to request sample verification.

Introduction: In this section, we present a challenging concept for the synthesis of an impurity associated with the brain metabolic activator citicoline—specifically, UDPC.
Citicoline serves as a crucial brain metabolic activator and is a derivative of nucleic acids, functioning as a key coenzyme in the synthesis of ovophosphorate. It facilitates cerebral cell respiration, enhances cognitive function, augments the activity of the ascending reticular activating system to promote alertness, reduces cerebrovascular resistance, and thereby improves cerebral blood circulation. This results in alleviation of cerebral hypoxia and optimization of brain matter metabolism; thus, it plays an essential role in human biofilm construction. Clinically, citicoline is primarily employed to address neurological sequelae resulting from traumatic brain injury and cerebrovascular accidents.
Today, we are pleased to present our innovative strategies for the synthesis of Uridine Diphosphate Choline (UDPC), aimed at addressing several challenges encountered in the synthesis process. Through diligent efforts and ongoing experimental exploration, we have achieved significant breakthroughs.

Figure 1: conceptual framework for UDPC Synthesis
As a significant bioactive compound, UDPC exhibits considerable potential for application in the medical field. However, previous synthesis methods have presented challenges such as low yield, complex procedures, and extended time requirements. To address these issues, we have achieved notable advancements through comprehensive research and the implementation of innovative synthetic strategies.
esterification parameters. Following extensive experimentation and comparative analysis, we ultimately identified the best activation reagent, resulting in a substantial enhancement of synthesis yield. This screening process is both intricate and crucial, laying a robust foundation for our subsequent research endeavors. The optimized reaction conditions have increased yield from 18% to 52%. By enhancing the purity of the crude product, subsequent purification operations are rendered significantly simpler.

Figure 2: roadmap for UDPC synthesis
By meticulously controlling the reaction time and concentration of hydrochloric methanol, we can effectively eliminate the protective groups on the two hydroxyl moieties, yielding UDPC with approximately 86% purity. While certain fractions exceeding 95% purity can be enriched through reverse preparative chromatography, this method significantly escalates the production costs associated with UDPC products. Ultimately, through iterative exploration of recrystallization protocols, we systematically evaluated 16 solvent systems; notably, a subset of ternary solvent systems successfully addressed this challenge. Through continuous experimentation and optimization, we identified that a critical control factor is the pH level of the product. Only within a specific pH range can efficient purification be achieved swiftly. This finding holds substantial implications for enhancing purity and expediting operational processes.
Through our dedicated efforts and innovative approaches, we have effectively addressed the complex challenges associated with UDPC synthesis and proposed a viable synthesis strategy. This significant breakthrough not only provided a substantial impetus for the development and production of related products but also established a robust foundation for our future research endeavors.
In addition to the structural confirmatory data obtained from nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry, the UDPC was also identified and validated in strict accordance with the USP methodology. The specific findings are as follows: Citicoline contains three primary specific impurities as outlined in the USP standard. Detailed methodologies, impurity profiles, and mixed injection data are presented in Figure 3-5.

Figure 3: chromatographic conditions as per the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) standards
Source: United States Pharmacopeia USP-NF2021

Figure 4: enumeration of specific impurities as outlined in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP)
Source: United States Pharmacopeia USP-NF2021

Figure 5: data on mixed UDPC and citicoline injections analyzed according to USP methodology

Figure 6: NMR hydrogen spectrum data for this batch of UDPC samples
As illustrated in FIG. 5, the relative retention time (RRT) of UDPC, measured at the QCS Standard Product R&D Center using the USP method, is recorded as 1.28. Furthermore, based on the data presented in FIG. 4, the RRT of UDPC under the USP methodology is noted to be 1.3; thus, the current test results align with established standards.
In conclusion, we would like to express our heartfelt gratitude to every member of the QCS R&D Center for their diligent efforts and unwavering commitment. It is through the collective endeavor and insights of all that we have successfully developed this innovative strategy. We anticipate that our research findings will provide greater inspiration and opportunities for industry development and application. We warmly invite customers to request sample verification.

Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号