Time:2024-08-16
introduction
Today we will share a study on the stability of specific impurities in the antibiotic Lincomycin. Lincomycin is a lincosamide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lincoides, which acts on sensitive bacterial ribosomes by binding to the central loop of the 50S subunit 23S rRNA gene, preventing peptide chain elongation and inhibiting protein synthesis in bacterial cells. Mainly used to treat chronic respiratory diseases in chickens and infections caused by penicillin G resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus.
Experimental scheme
In this experiment, our center conducted a systematic applicability experiment on our laboratory's chromatographic system, referring to the chromatographic conditions under the "Related substances" item of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition, and the solution stability of two specific impurities of Lincomycin was studied, the sample item numbers and structural formulas used in the system suitability experiment are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, and the sample item numbers and structural formulas used in the stability study of specific impurity solutions are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4:
System Applicability Experiment
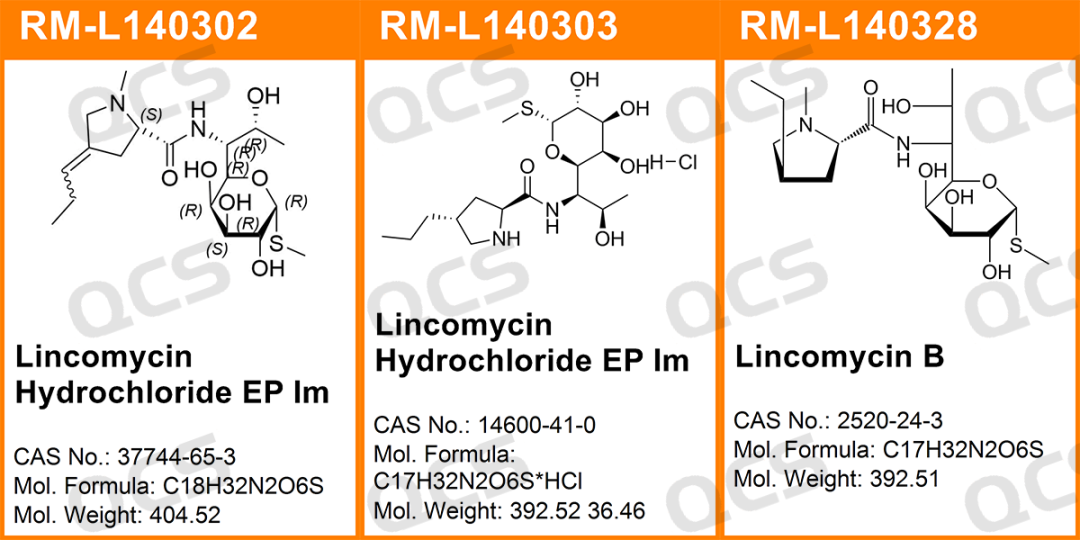
Figure 1: Impurity item number and structural formula used in the system suitability experiment
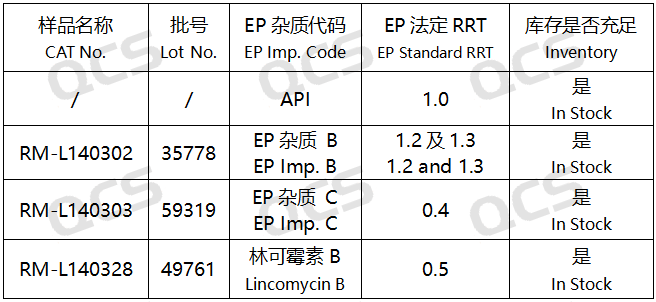
Figure 2: Correspondence diagram between pharmacopoeia impurity codes and system suitability product QCS item numbers
stability of solution
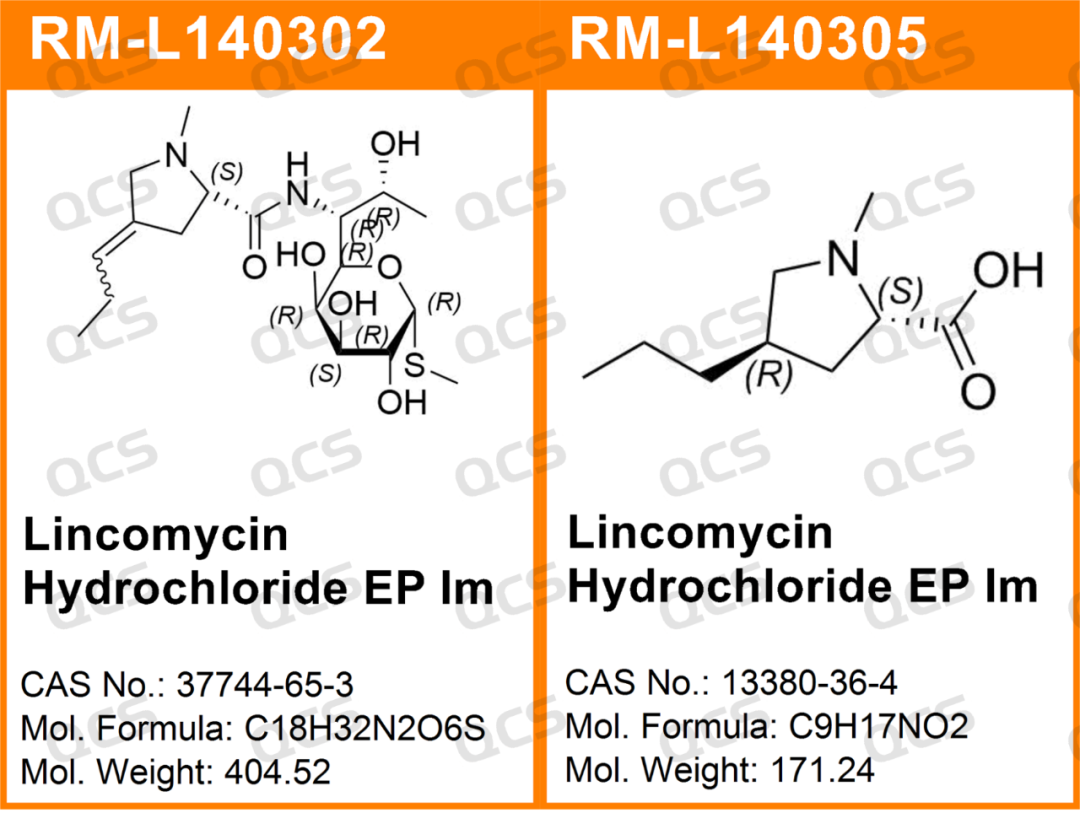
Figure 3: Sample item number and structural formula used for stability study of specific impurity solutions
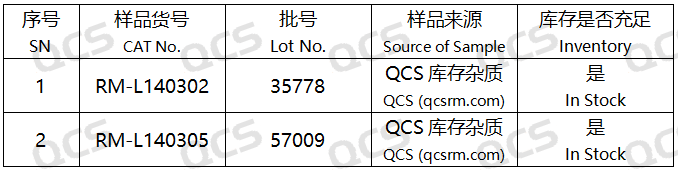
Figure 4: Statistical table of sample item numbers used for stability study of specific impurity solutions
In this experiment, the experimenter first conducted liquid phase localization experiments on samples RM-L140302 (Lincomycin Hydrochloride EP Impurity B, CAS:37744-65-3)、RM-L140303 (Lincomycin Hydrochloride EP Impurity C, CAS:14600-41-0) and RM-L140328 (Lincomycin B, CAS:2520-24-3) under the chromatographic conditions of the "Related substances" item in the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety item of the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition. By comparing the relative retention times of RM-L140302 (EP impurity B), RM-L140303 (EP impurity C), and RM-L140328 (Lincomycin B) with the relative retention times recorded in the pharmacopoeia, we aim to assess the suitability of our laboratory's liquid-phase system. Then take appropriate amounts of RM-L140302 and RM-L140305, and place them in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions, respectively. Place them at room temperature and pressure for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours, respectively. Follow the chromatographic conditions used in the "Related substances" section of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety item in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition for injection detection. The stability of the sample solution was determined by observing the change of the main peak area in the chromatogram with the extension of the storage time of the sample solution. However, during the actual measurement process, the experimenter found that RM-L140305 was not suitable for detection using the chromatographic conditions used under the "Related substances" item of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition. Therefore, the following method was used for detection instead:
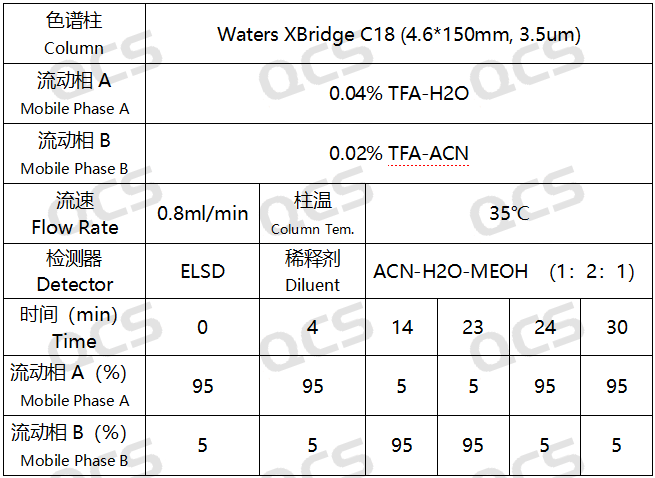
Figure 5: Stability testing method for sample RM-L140305 solution
Experimental data
System applicability experiment
After testing, it was found that the relative retention times (RRT) obtained from the experiments of RM-L140302 (EP impurity B), RM-L140303 (EP impurity C), and RM-L140328 (Lincomycin B) were consistent with the relative retention times recorded under the "Related substances" item of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition. So it can be considered that the liquid phase system in this laboratory has good applicability. The experimental data are shown in Figures 6 and 7:
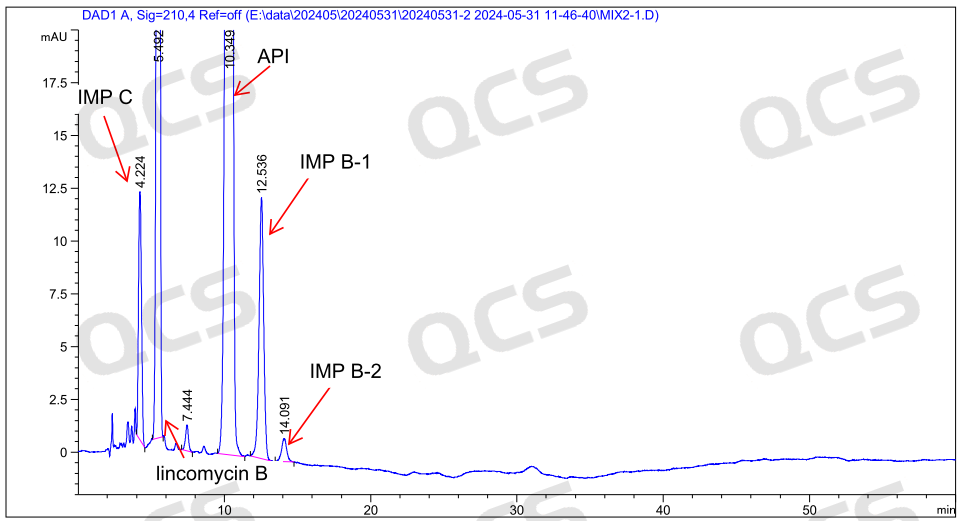
Figure 6: The mixed injection chromatogram of the active pharmaceutical ingredient and three impurities included in the "Related substances" section of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety item in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition
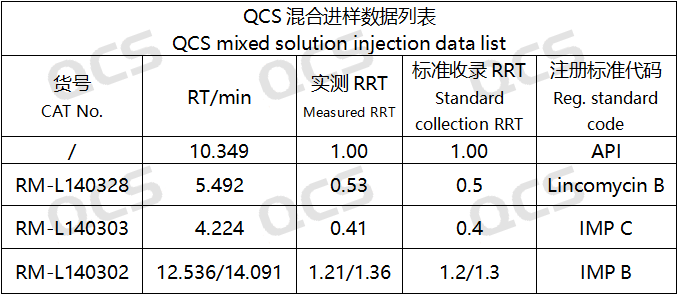
Figure 7: Summary of applicability data for liquid phase systems
Stability experiment of impurity solution
After testing, it was found that the main peak area of sample RM-L140302 did not change significantly after being placed in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions for 24 hours, and the relative standard deviation was less than 2.0%. Therefore, it can be considered that the sample is relatively stable in acidic, neutral and alkaline solutions for 24 hours. During the 24-hour storage of sample RM-L140305 in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions, although the relative standard deviation of the main peak area of the sample was greater than 2.0%, no major impurities were produced in the spectrum, and the main peak area did not gradually decrease. So it can be considered that the sample is also relatively stable when placed in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions for 24 hours. The main peak area data of each detection point for RM-L140302 and RM-L140305 under different pH conditions are as follows:
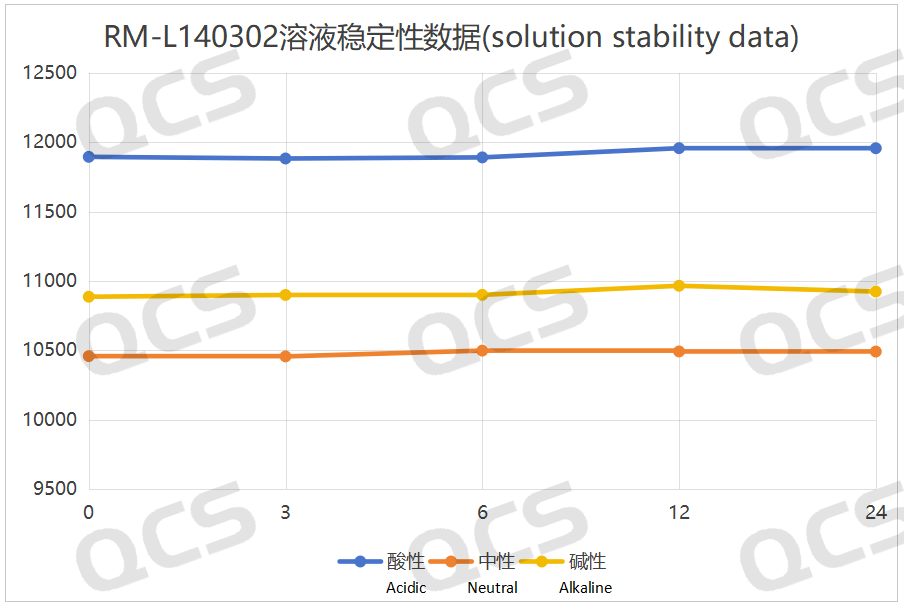
Figure 8: Summary line chart of solution stability data for sample RM-L140302
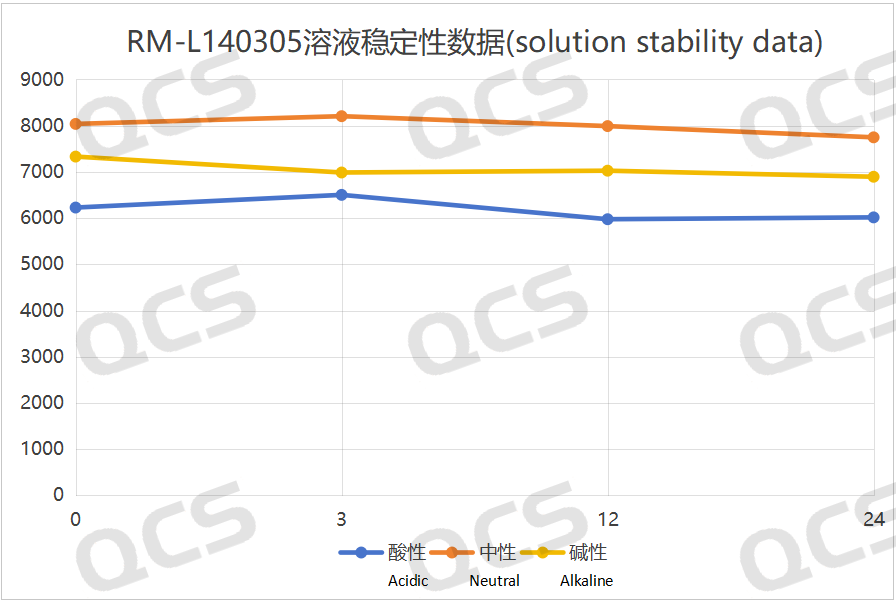
Figure 9: Summary line chart of solution stability data for sample RM-L140305
Experiment conclusion
In summary, through this experiment, we found that samples RM-L140302 and RM-L140305 have good stability in acidic, alkaline, and neutral solutions. If customers have a need for the stability of these two samples, welcome to consult our company.


introduction
Today we will share a study on the stability of specific impurities in the antibiotic Lincomycin. Lincomycin is a lincosamide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lincoides, which acts on sensitive bacterial ribosomes by binding to the central loop of the 50S subunit 23S rRNA gene, preventing peptide chain elongation and inhibiting protein synthesis in bacterial cells. Mainly used to treat chronic respiratory diseases in chickens and infections caused by penicillin G resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus.
Experimental scheme
In this experiment, our center conducted a systematic applicability experiment on our laboratory's chromatographic system, referring to the chromatographic conditions under the "Related substances" item of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition, and the solution stability of two specific impurities of Lincomycin was studied, the sample item numbers and structural formulas used in the system suitability experiment are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, and the sample item numbers and structural formulas used in the stability study of specific impurity solutions are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4:
System Applicability Experiment

Figure 1: Impurity item number and structural formula used in the system suitability experiment

Figure 2: Correspondence diagram between pharmacopoeia impurity codes and system suitability product QCS item numbers
stability of solution

Figure 3: Sample item number and structural formula used for stability study of specific impurity solutions

Figure 4: Statistical table of sample item numbers used for stability study of specific impurity solutions
In this experiment, the experimenter first conducted liquid phase localization experiments on samples RM-L140302 (Lincomycin Hydrochloride EP Impurity B, CAS:37744-65-3)、RM-L140303 (Lincomycin Hydrochloride EP Impurity C, CAS:14600-41-0) and RM-L140328 (Lincomycin B, CAS:2520-24-3) under the chromatographic conditions of the "Related substances" item in the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety item of the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition. By comparing the relative retention times of RM-L140302 (EP impurity B), RM-L140303 (EP impurity C), and RM-L140328 (Lincomycin B) with the relative retention times recorded in the pharmacopoeia, we aim to assess the suitability of our laboratory's liquid-phase system. Then take appropriate amounts of RM-L140302 and RM-L140305, and place them in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions, respectively. Place them at room temperature and pressure for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours, respectively. Follow the chromatographic conditions used in the "Related substances" section of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety item in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition for injection detection. The stability of the sample solution was determined by observing the change of the main peak area in the chromatogram with the extension of the storage time of the sample solution. However, during the actual measurement process, the experimenter found that RM-L140305 was not suitable for detection using the chromatographic conditions used under the "Related substances" item of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition. Therefore, the following method was used for detection instead:

Figure 5: Stability testing method for sample RM-L140305 solution
Experimental data
System applicability experiment
After testing, it was found that the relative retention times (RRT) obtained from the experiments of RM-L140302 (EP impurity B), RM-L140303 (EP impurity C), and RM-L140328 (Lincomycin B) were consistent with the relative retention times recorded under the "Related substances" item of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition. So it can be considered that the liquid phase system in this laboratory has good applicability. The experimental data are shown in Figures 6 and 7:

Figure 6: The mixed injection chromatogram of the active pharmaceutical ingredient and three impurities included in the "Related substances" section of the "LINCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE" variety item in the European Pharmacopoeia 11.0 edition

Figure 7: Summary of applicability data for liquid phase systems
Stability experiment of impurity solution
After testing, it was found that the main peak area of sample RM-L140302 did not change significantly after being placed in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions for 24 hours, and the relative standard deviation was less than 2.0%. Therefore, it can be considered that the sample is relatively stable in acidic, neutral and alkaline solutions for 24 hours. During the 24-hour storage of sample RM-L140305 in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions, although the relative standard deviation of the main peak area of the sample was greater than 2.0%, no major impurities were produced in the spectrum, and the main peak area did not gradually decrease. So it can be considered that the sample is also relatively stable when placed in acidic, neutral, and alkaline solutions for 24 hours. The main peak area data of each detection point for RM-L140302 and RM-L140305 under different pH conditions are as follows:

Figure 8: Summary line chart of solution stability data for sample RM-L140302

Figure 9: Summary line chart of solution stability data for sample RM-L140305
Experiment conclusion
In summary, through this experiment, we found that samples RM-L140302 and RM-L140305 have good stability in acidic, alkaline, and neutral solutions. If customers have a need for the stability of these two samples, welcome to consult our company.


Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号