Time:2023-12-08
Introduction: Today, we present our research on impurities associated with the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria using Pelastine tablets, a popular product manufactured by FAES FARMA Company. Currently, domestic Pelastine preparations and raw materials have received one registration approval number, comprising one preparation approval number and no approval letter for raw materials.
Bilastine is a non-sedating, long-acting antihistamine that selectively antagonizes peripheral H1 receptors with low affinity for muscarinic receptors and other receptors. It is indicated for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria, including adults and adolescents aged 12 years and above.
As of now, a total of 53 impurities of Bilastine have been documented on the official QCS website (Scan the QR code at the end of this article to access the complete list of impurities). Our center has conducted relevant research on the primary impurities of Bilastine in accordance with the import registration standard for Bilastine Tablets (standard number JX20130329). The structural information for both raw material impurities and specific customer-focused impurities is presented in Figure 1.
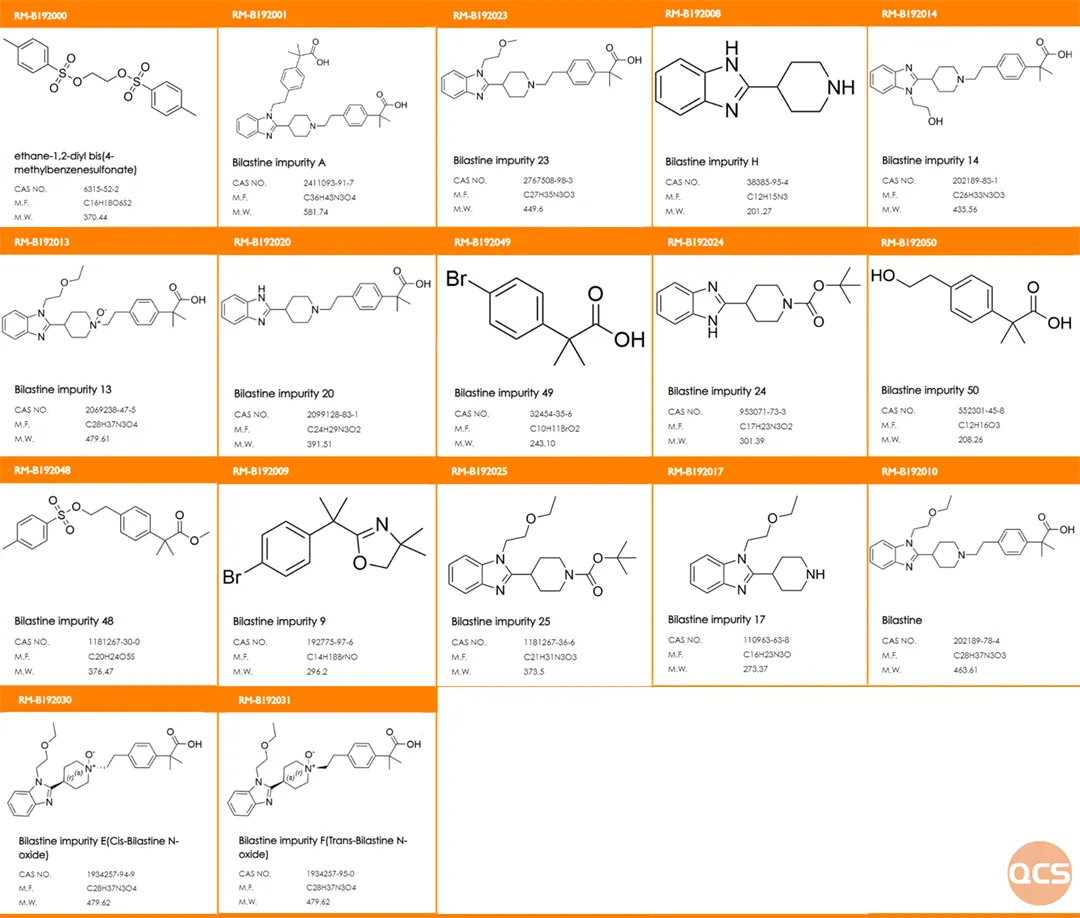
Figure 1: List of Key Impurities for Bilastin Customers
According to the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (Standard No. JX20130329), our center mainly conducted qualitative and quantitative research on the following 16 impurities. During the experiment, it was found that RM-B192020 and RM-B192031 could not be separated on the chromatographic conditions specified in the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (Standard No. JX20130329) (see Figure 2). Therefore, the chromatographic conditions in the standard were adjusted (the mobile phase was changed from MeOH-ACN-Buffer (32.5:30:37.5) to MeOH-ACN-Buffer (32.5:28.1:39.4), the Buffer content is specified in the chromatographic conditions for the impurities check in the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (Standard No. JX20130329), the other conditions remain unchanged). The specific standard code impurity and QCS lot number correspondence is shown in Figure 4, and the chromatographic data for verifying the code impurity are shown in Figures 5 and 6.
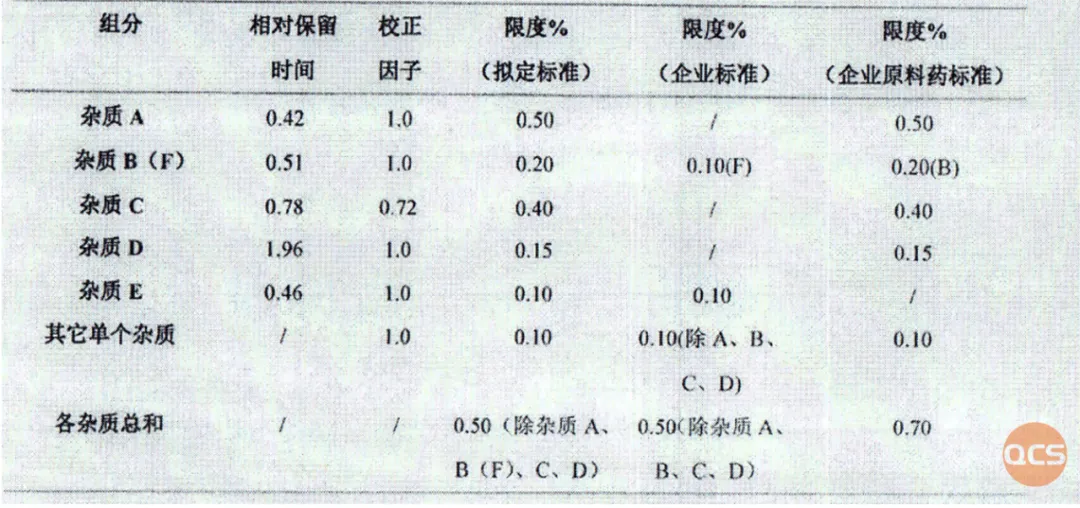
Figure 2: Related information on impurities included in the verification standard
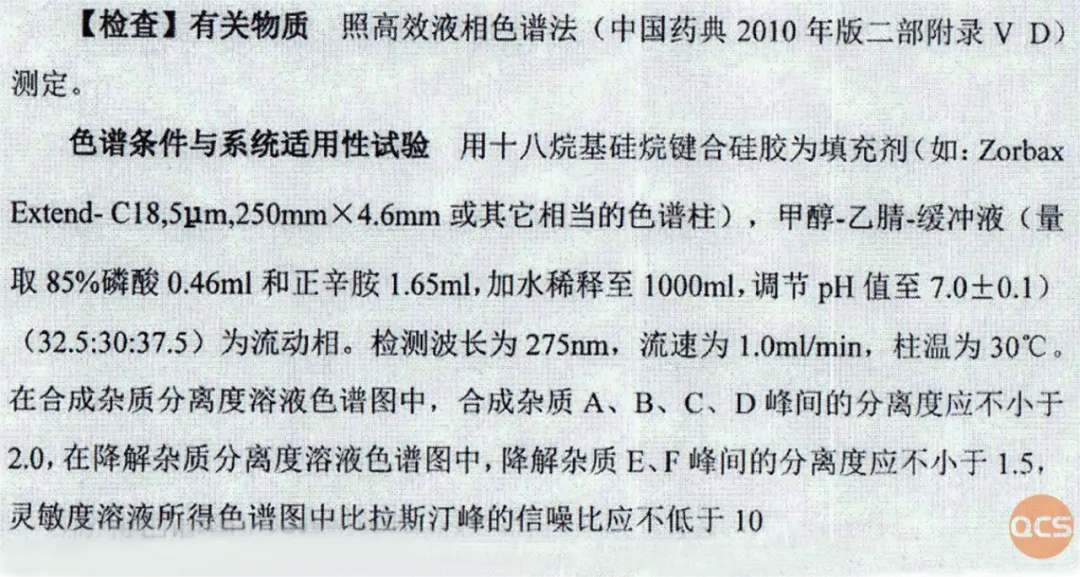
Figure 3: Related substances section of the verification criteria
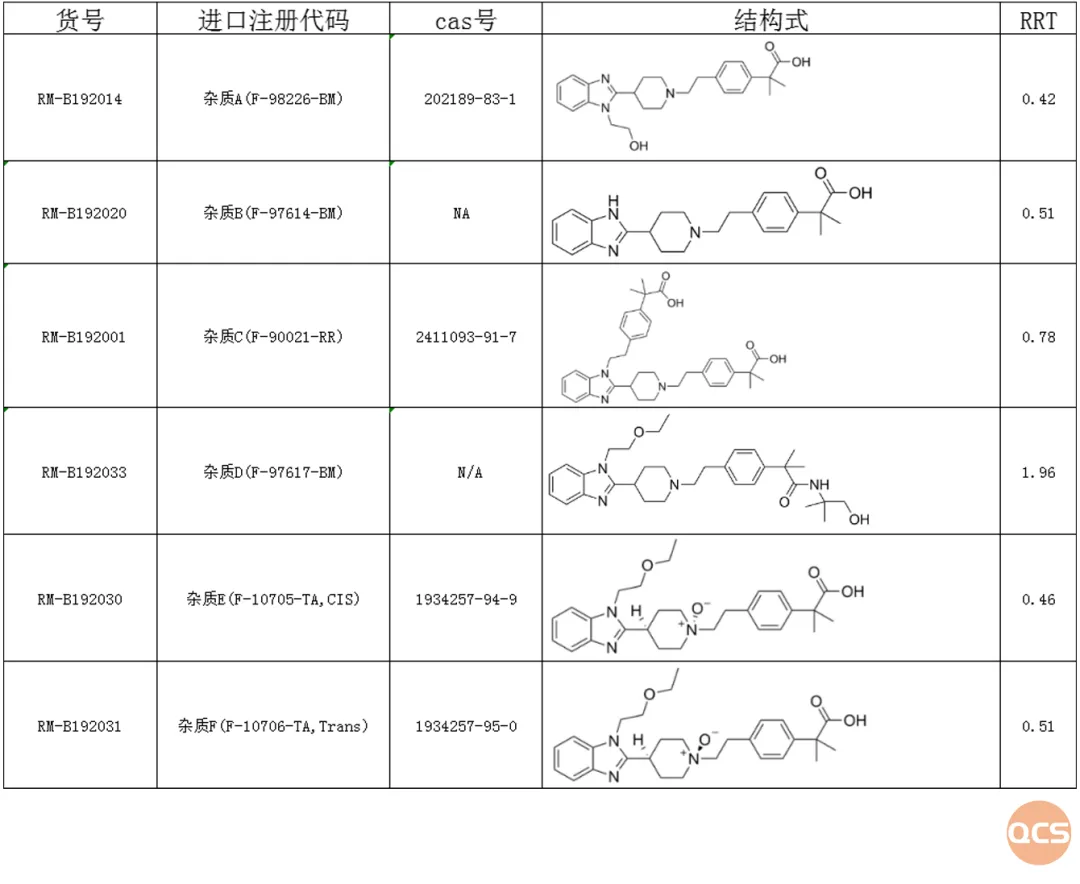
Figure 4: Standard Code Defects and QCS Article Number Correspondence Relationship
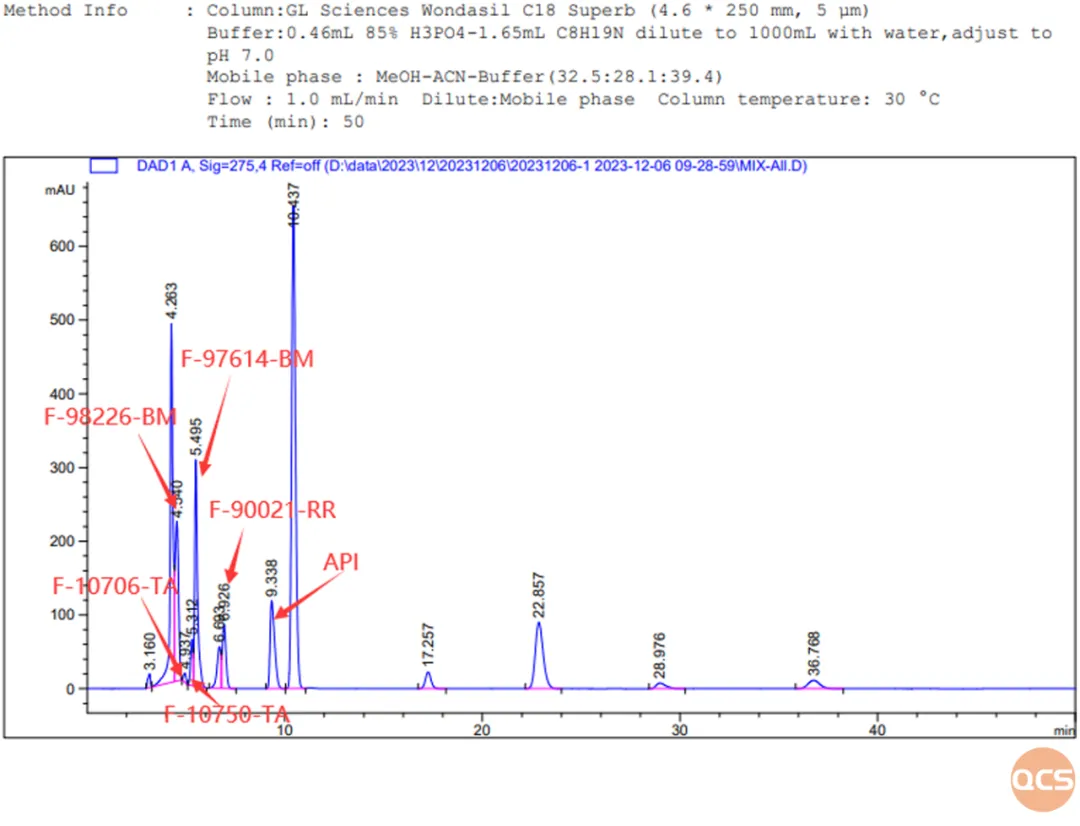
Figure 5: Chromatogram and data summary of 16 impurities and API of Bilastin
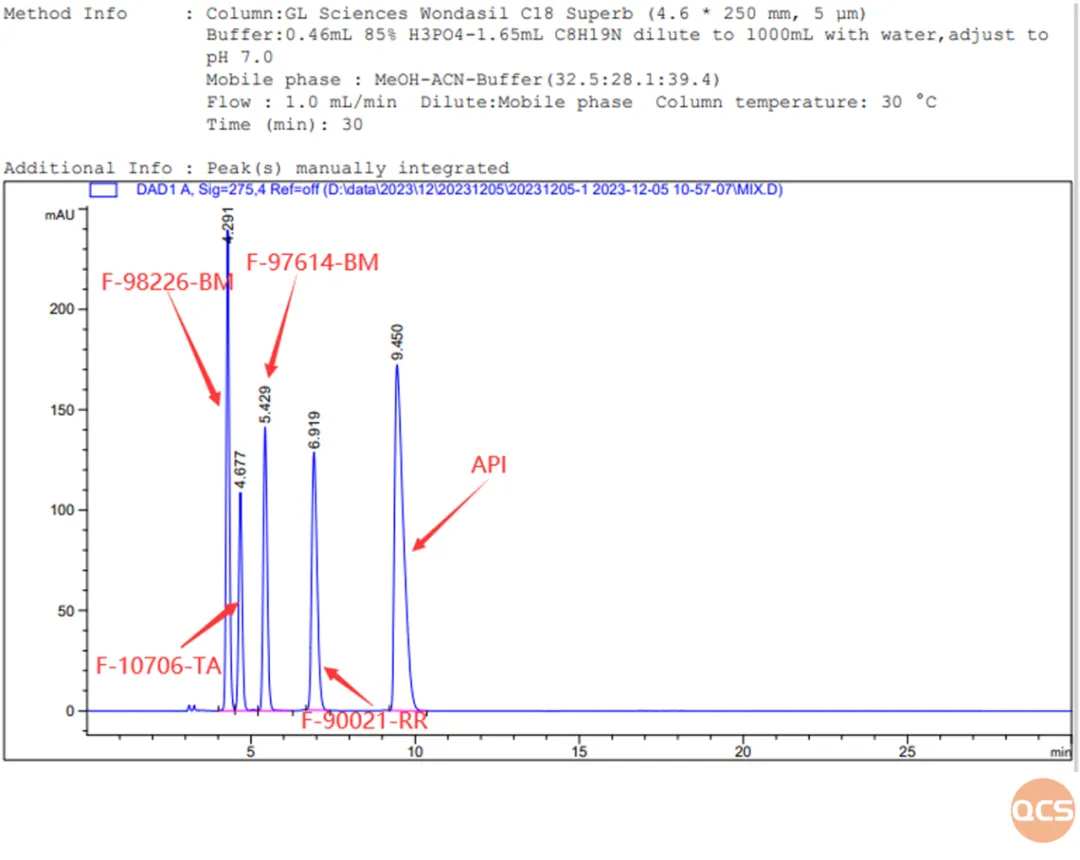
Figure 6: 4 impurity identification chromatograms and data summaries according to the registration standard
In this study, the QCS R&D Center selected 16 impurity products and API products in stock for a series of studies and calculated the relative retention time data for all impurity products (Figure 7). Although the stationary phase of the chromatography column used in this study was not exactly the same as the standard, and the proportion of the components in the mobile phase was slightly different, the measured relative retention times were basically consistent with the data in the standard (JX20130329), which includes the 4 impurity codes F-97617-BM and F-10705-TA, as the criteria. It can be considered that the chromatographic results of the imported registration standard have been basically reproduced in this study. The specific data are shown in Figure 8:
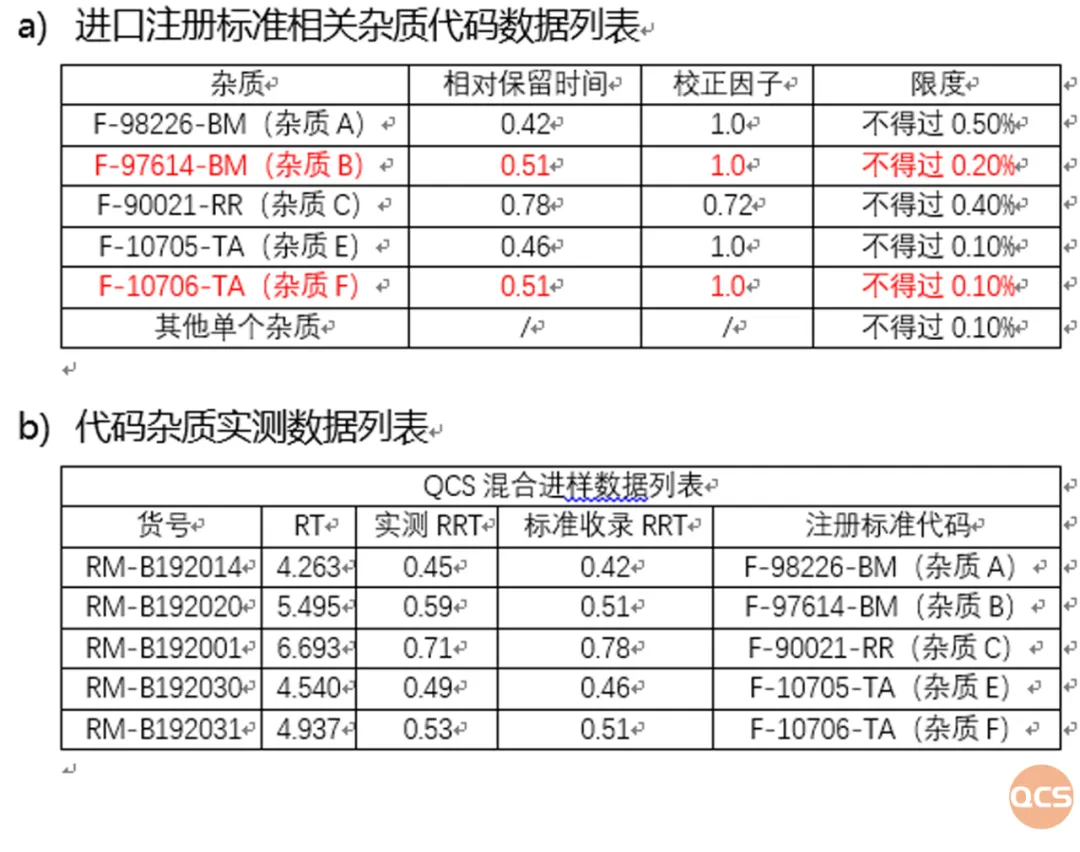
Figure 7: Code impurity-related standards and verification data in import registration standards
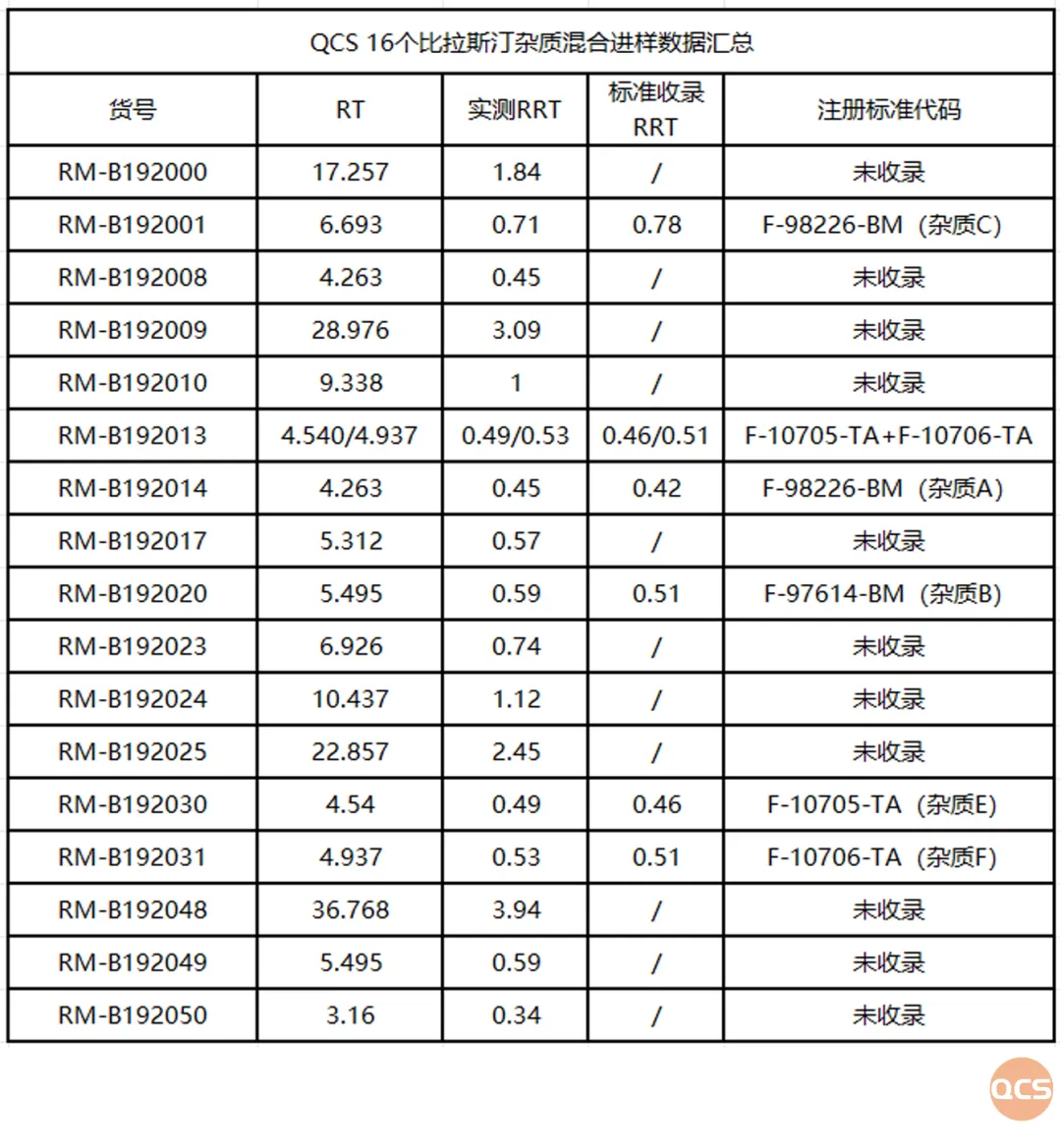
Figure 8: 16 Impurity Profiling Chromatograms and Data Summary
The purpose of this study was to conduct a comparative study of 16 products from the QCS standard material development center under uniform chromatographic conditions. From the data in Figure 5, it can be seen that when 16 impurities and the API are injected simultaneously under the same chromatographic conditions, some impurities may co-elute and cannot be effectively separated, such as RM-B1920 (08&14), RM-B1920 (13&30), RM-B1920 (13&31), RM-B1920 (20&49). Among them, RM-B192030 (impurity E) and RM-B192031 (impurity F) are diastereoisomers, and in Figure 5, these diastereoisomers cannot be well separated, but can be well separated when injected separately. Other impurities that cannot be separated in Figure 5 can also be well separated when injected separately.
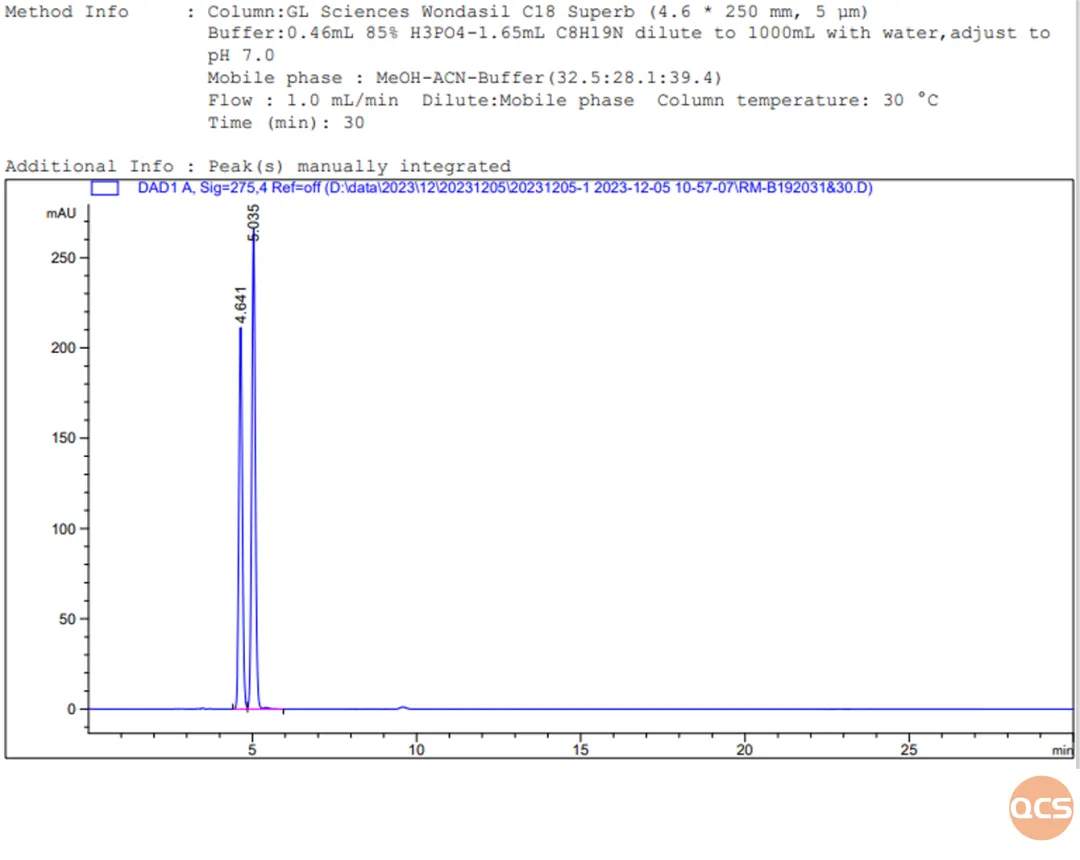
Figure 9: Chromatogram of impurities E (Cis N-oxide) and F (Trans N-oxide) mixed for injection
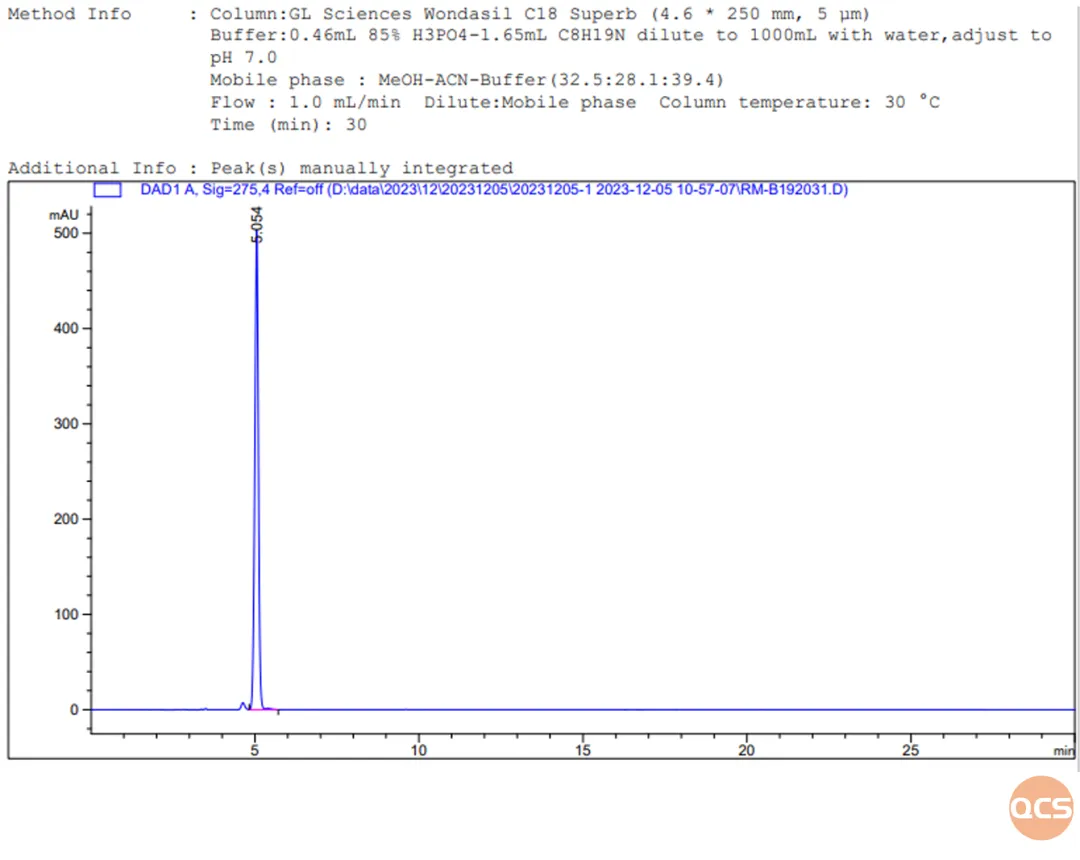
Figure 10: Chromatogram of RM-B192031 taken individually
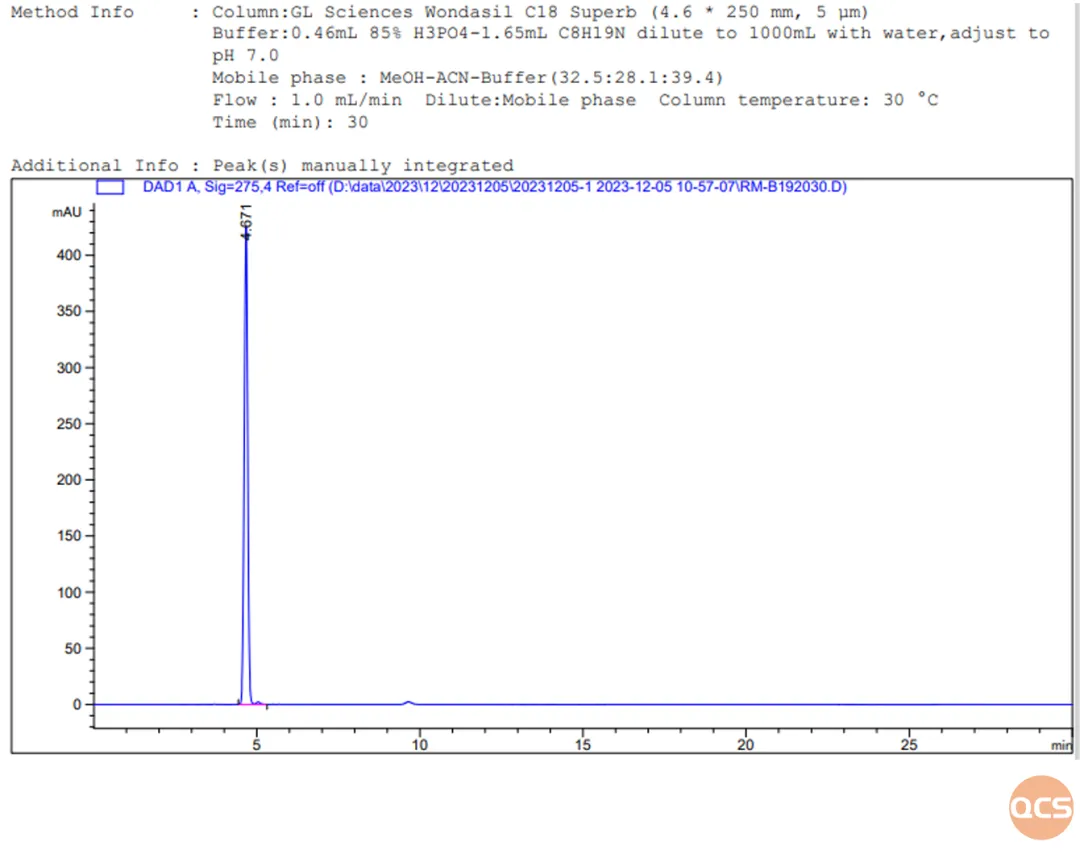
Figure 11: Chromatogram of RM-B192030 taken individually
RM-B192031 and RM-B192020 are impurity substances included in the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (standard number JX20130329). Their respective codes are F-10706-TA (impurity F) and F-97614-BM (impurity B). These two impurities cannot be separated on the chromatographic conditions specified in the import registration standard for related substances. After adjusting the mobile phase, our center was able to achieve baseline separation of the two impurities, as shown in Figure 12.
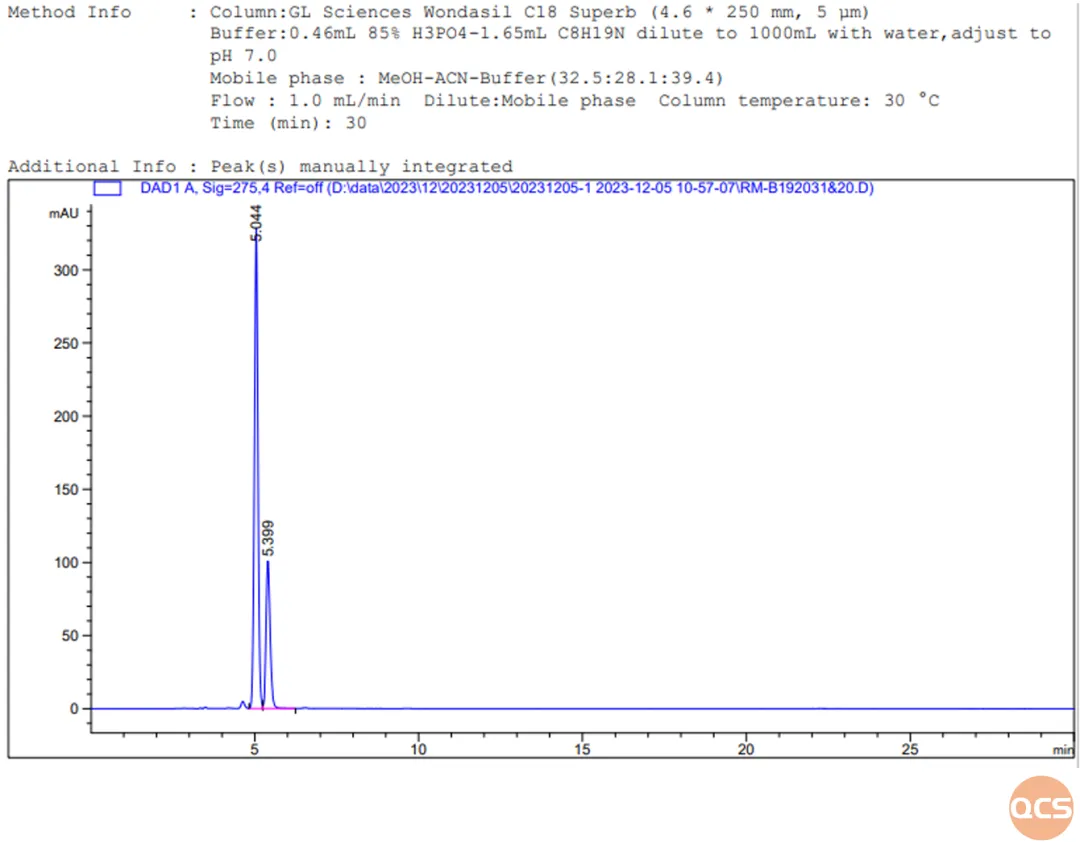
Figure 12: Chromatogram of RM-B192020 mixed with RM-B192031
It is evident from the above data that multi-sample mixed injection may introduce certain interference with the chromatographic results. In order to provide more comprehensive chromatographic reference information, the QCS Standard Material Research and Development Center has conducted individual sample injection tests for 16 impurity products in addition to separate sample tests, aiming to offer a more comprehensive reference than Rastin impurity research by combining the results of individual and mixed sample tests.
Long press to recognize the QR code and view the complete list of impurities!



Introduction: Today, we present our research on impurities associated with the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria using Pelastine tablets, a popular product manufactured by FAES FARMA Company. Currently, domestic Pelastine preparations and raw materials have received one registration approval number, comprising one preparation approval number and no approval letter for raw materials.
Bilastine is a non-sedating, long-acting antihistamine that selectively antagonizes peripheral H1 receptors with low affinity for muscarinic receptors and other receptors. It is indicated for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria, including adults and adolescents aged 12 years and above.
As of now, a total of 53 impurities of Bilastine have been documented on the official QCS website (Scan the QR code at the end of this article to access the complete list of impurities). Our center has conducted relevant research on the primary impurities of Bilastine in accordance with the import registration standard for Bilastine Tablets (standard number JX20130329). The structural information for both raw material impurities and specific customer-focused impurities is presented in Figure 1.

Figure 1: List of Key Impurities for Bilastin Customers
According to the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (Standard No. JX20130329), our center mainly conducted qualitative and quantitative research on the following 16 impurities. During the experiment, it was found that RM-B192020 and RM-B192031 could not be separated on the chromatographic conditions specified in the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (Standard No. JX20130329) (see Figure 2). Therefore, the chromatographic conditions in the standard were adjusted (the mobile phase was changed from MeOH-ACN-Buffer (32.5:30:37.5) to MeOH-ACN-Buffer (32.5:28.1:39.4), the Buffer content is specified in the chromatographic conditions for the impurities check in the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (Standard No. JX20130329), the other conditions remain unchanged). The specific standard code impurity and QCS lot number correspondence is shown in Figure 4, and the chromatographic data for verifying the code impurity are shown in Figures 5 and 6.

Figure 2: Related information on impurities included in the verification standard

Figure 3: Related substances section of the verification criteria

Figure 4: Standard Code Defects and QCS Article Number Correspondence Relationship

Figure 5: Chromatogram and data summary of 16 impurities and API of Bilastin

Figure 6: 4 impurity identification chromatograms and data summaries according to the registration standard
In this study, the QCS R&D Center selected 16 impurity products and API products in stock for a series of studies and calculated the relative retention time data for all impurity products (Figure 7). Although the stationary phase of the chromatography column used in this study was not exactly the same as the standard, and the proportion of the components in the mobile phase was slightly different, the measured relative retention times were basically consistent with the data in the standard (JX20130329), which includes the 4 impurity codes F-97617-BM and F-10705-TA, as the criteria. It can be considered that the chromatographic results of the imported registration standard have been basically reproduced in this study. The specific data are shown in Figure 8:

Figure 7: Code impurity-related standards and verification data in import registration standards

Figure 8: 16 Impurity Profiling Chromatograms and Data Summary
The purpose of this study was to conduct a comparative study of 16 products from the QCS standard material development center under uniform chromatographic conditions. From the data in Figure 5, it can be seen that when 16 impurities and the API are injected simultaneously under the same chromatographic conditions, some impurities may co-elute and cannot be effectively separated, such as RM-B1920 (08&14), RM-B1920 (13&30), RM-B1920 (13&31), RM-B1920 (20&49). Among them, RM-B192030 (impurity E) and RM-B192031 (impurity F) are diastereoisomers, and in Figure 5, these diastereoisomers cannot be well separated, but can be well separated when injected separately. Other impurities that cannot be separated in Figure 5 can also be well separated when injected separately.

Figure 9: Chromatogram of impurities E (Cis N-oxide) and F (Trans N-oxide) mixed for injection

Figure 10: Chromatogram of RM-B192031 taken individually

Figure 11: Chromatogram of RM-B192030 taken individually
RM-B192031 and RM-B192020 are impurity substances included in the import registration standard for Bilastin Tablets (standard number JX20130329). Their respective codes are F-10706-TA (impurity F) and F-97614-BM (impurity B). These two impurities cannot be separated on the chromatographic conditions specified in the import registration standard for related substances. After adjusting the mobile phase, our center was able to achieve baseline separation of the two impurities, as shown in Figure 12.

Figure 12: Chromatogram of RM-B192020 mixed with RM-B192031
It is evident from the above data that multi-sample mixed injection may introduce certain interference with the chromatographic results. In order to provide more comprehensive chromatographic reference information, the QCS Standard Material Research and Development Center has conducted individual sample injection tests for 16 impurity products in addition to separate sample tests, aiming to offer a more comprehensive reference than Rastin impurity research by combining the results of individual and mixed sample tests.
Long press to recognize the QR code and view the complete list of impurities!



Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号