Time:2024-05-16
01 Introduction
Today, we would like to share the data of Amlodipine-specific impurity stability research to provide data support for customers in the storage and use of related impurities. Judging from our current stability data, the product will indeed have a relatively obvious degradation under certain conditions, please refer to the research data below for details.
02 Introduction to Amlodipine-related projects
Amlodipine is a long-acting calcium antagonist that lowers blood pressure by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into heart and smooth muscle cells. It can be used for the treatment of hypertension and alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs, and can also be used for the treatment of coronary heart disease, such as chronic stable angina、vasospasm angina. Amlodipine-related impurities are our company's advantageous product items, in addition to the above-mentioned products, there are nearly 30 kinds of drug-related impurities, our company has more than 20 kinds of impurities in stock, and products information is shown in Figure 1 below:
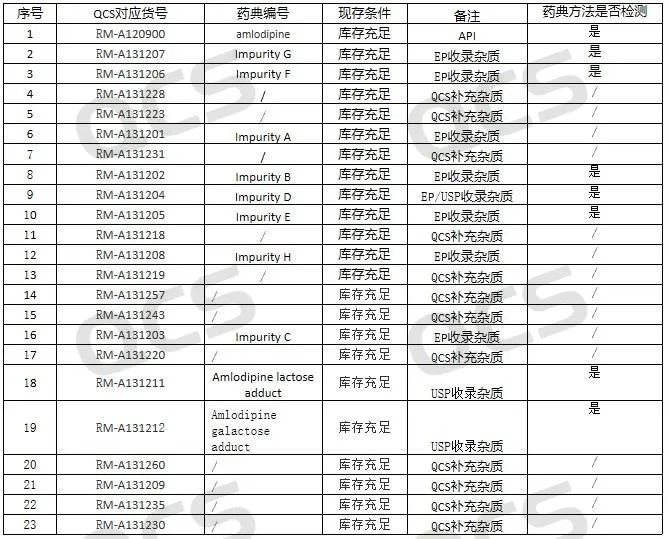
Figure 1: The correspondence between the impurity codes included in the API and the standard and our company's impurity article numbers
The structural formula of inventory impurities is shown in Figure 2:
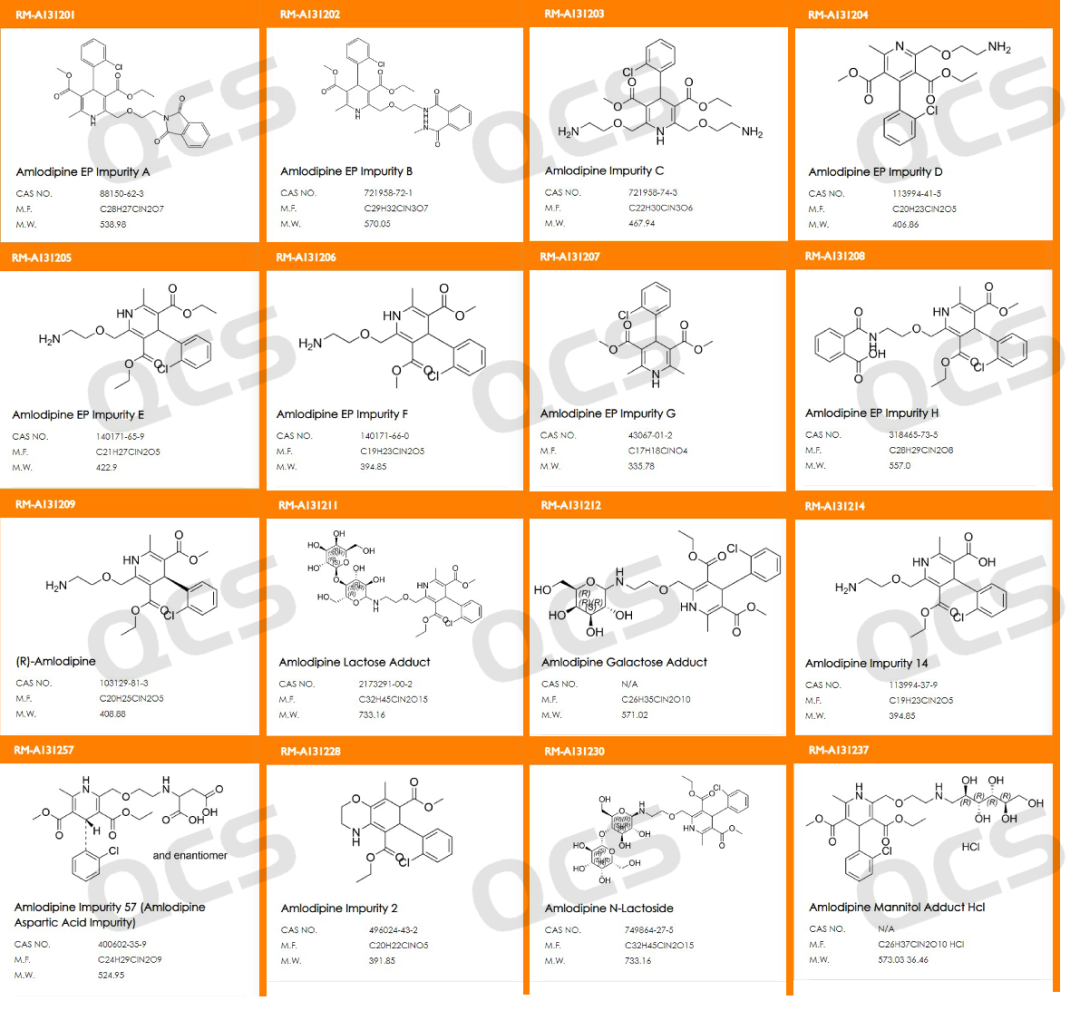
Figure 2: Structural formula of impurities included in API and QCS
03 Impurity localization studies
Our center conducted localization research on specific impurities first. By referring to the HPLC chromatographic conditions used in the《European Pharmacopoeia》 11.0 version 《AMODIPINE BESILATE》, conduct liquid chromatography localization studies on multiple impurities, including impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204) and impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205). The QCS R&D center conducted a series of studies on multiple impurity products and active pharmaceutical ingredients in stock, and calculated the relative retention time data of all impurity products. Our center has made appropriate adjustments to the EP conditions based on the existing chromatographic columns, and the measured relative retention time under these conditions is basically consistent with the data in the standard. It can be considered that the chromatographic results of the imported registration standard have been basically reproduced in this study. Due to space limitations, this article only extracts two impurity data for display (Figure 3-5) (If you have other data requirements, please contact the corresponding sales personnel).
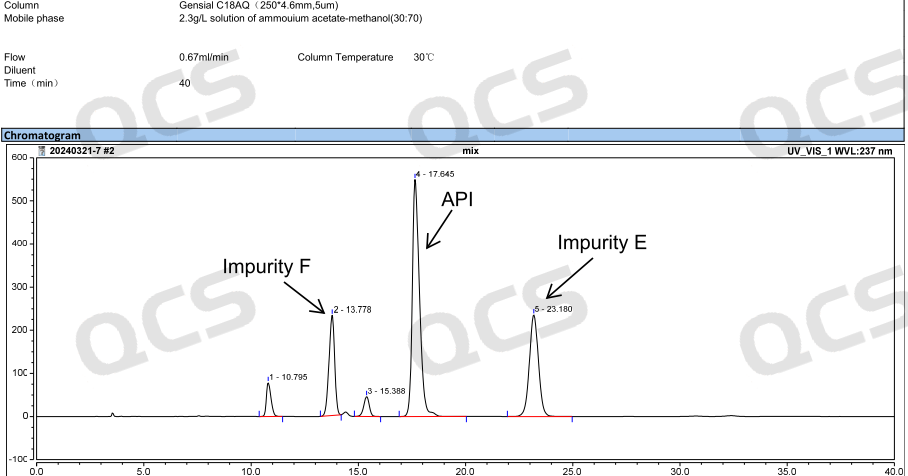
Figure 3: Chromatogram of mixed injection of API and some impurities
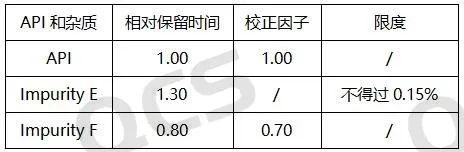
Figure 4: Data related to Amlodipine API and two impurities in the EP Pharmacopoeia
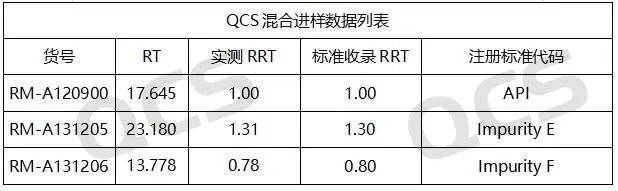
Figure 5: Summary of tested data for Amlodipine and impurity E, F
04 Impurity stability research
In addition to qualitative research, many customers have significant concerns about how impurities are stored, used, whether the product is stable, and whether the data is reliable. Due to the particularity of impurity reference materials, there is a risk of spoilage during storage, transportation, and use of the product. So customers are particularly concerned about how to prepare, store, and use the reserve liquid.
In order to better answer customer questions, our center has conducted relevant stability research on specific impurities. The stability research of the solution was conducted on behalf of EP standard impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204), impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205), and USP standard Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211). This research will provide positive reference for the use of relevant reference materials, stability time, and reliability of sample results, in order to solve the confusion of product storage and use stability.
The experimental design for this experiment is as follows: Take the sample to be studied, place the sample in solutions with pH=A, B, and C three acid-base gradients, and test at 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 hours, respectively. Summarize the purity test results of the samples over time under different solution conditions, which can effectively reflect the stability trend of the samples under these conditions. The summary of the main peak area data for each detection point under various pH conditions is shown in Figures 6-9:
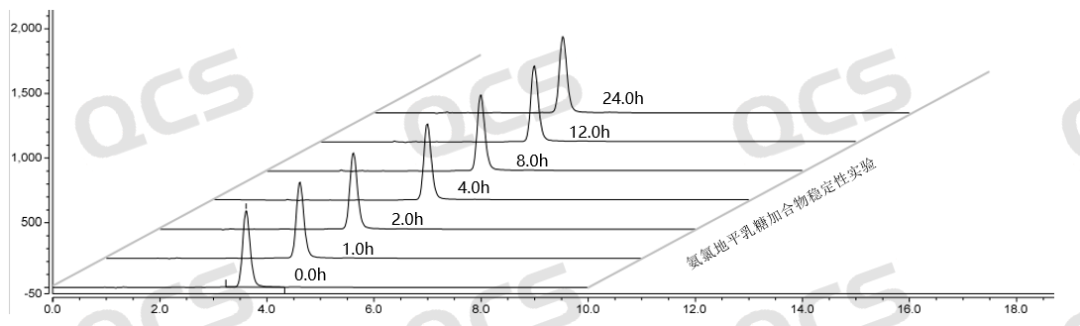
Figure 6: Summary of stability data for pH=A solution of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211)
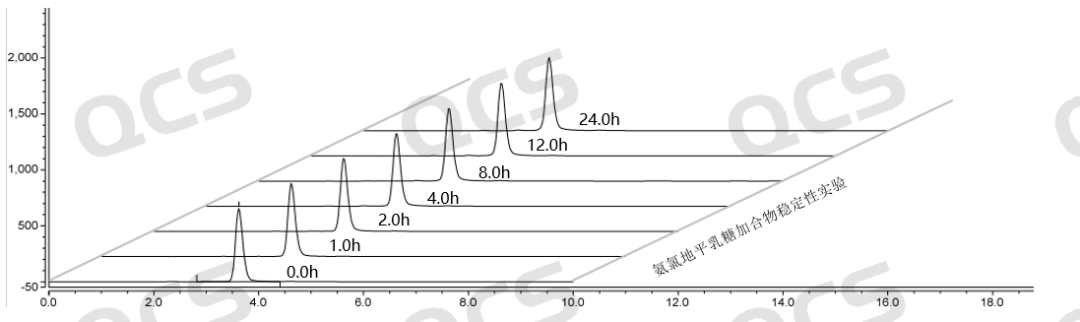
Figure 7: Summary of stability data for pH=B solution of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211)
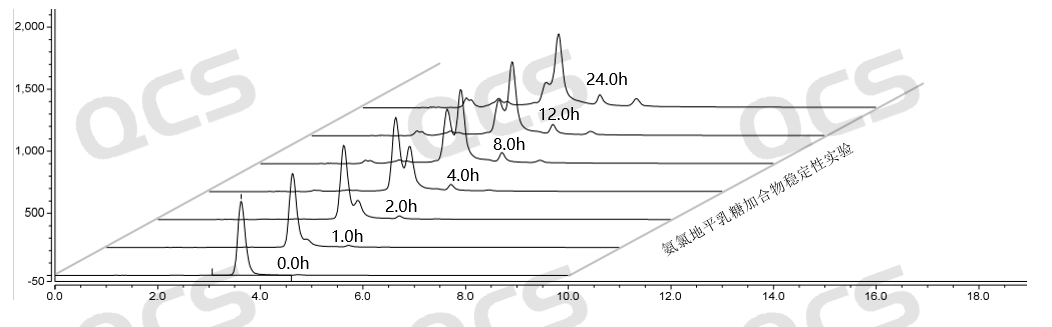
Figure 8: Summary of stability data for pH=C solution of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211)
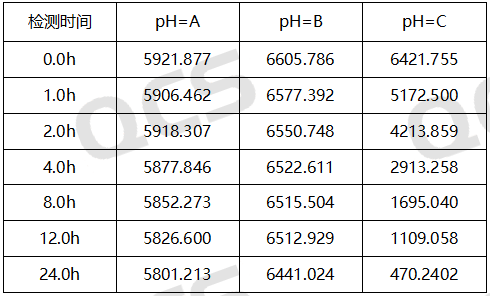
Figure 9: Summary of main peak area data for stability testing of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct(QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) solution
From the above data, it can be seen that the Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) was left in solutions pH=A and B for 24 hours respectively, and no obvious impurity peaks were detected. At the same time, the main peak area did not change much, indicating that the sample was relatively stable in solutions pH=A and B and did not degrade. However, during the placement of a solution with pH=C, a continuous decrease in the area of the main peak and an increase in the number of impurity peaks can be monitored. Especially during the process from 0.0h to 4.0h, the purity of the product showed a significant decrease, indicating that the Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) is very unstable under pH=C solution conditions and will quickly degrade. Based on the above experimental data, customers are advised to pay special attention to the acid-base conditions when using this impurity to avoid abnormal detection results.
In addition, our center also conducted the same research and testing on impurities D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204) and E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205), the results are summarized in the following figure (10-12):
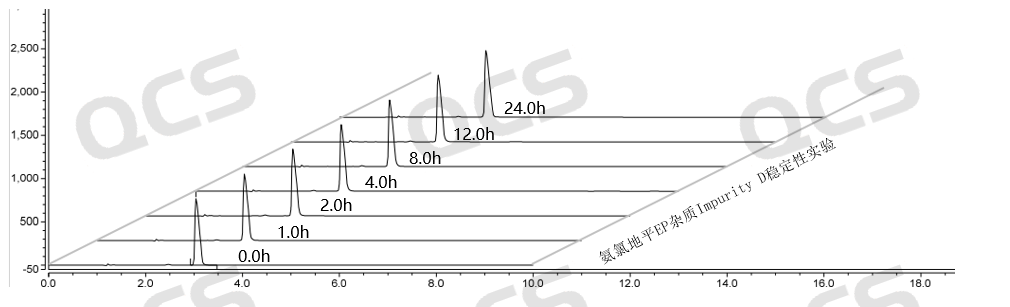
Figure 10: Summary of stability data for pH=A solution of EP Impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204)
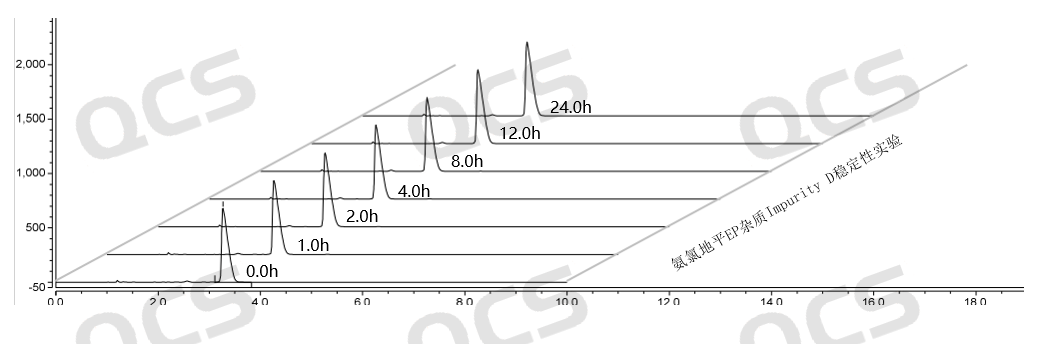
Figure 11: Summary of stability data for pH=B solution of EP Impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204)
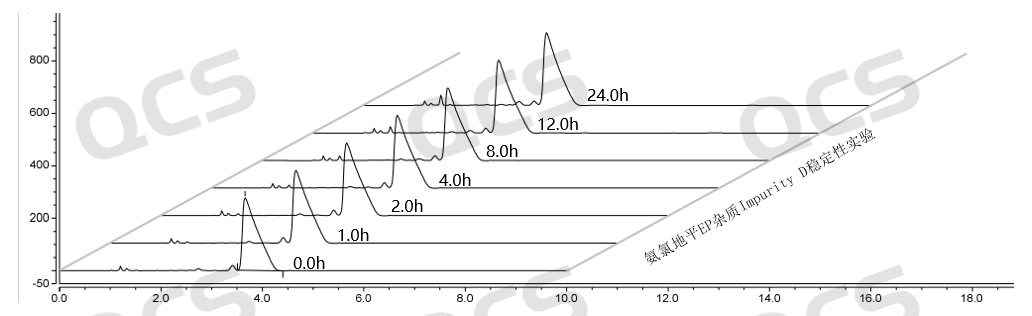
Figure 12: Summary of stability data for pH=C solution of EP Impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204)
As can be seen from Figure 10-12, impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204) was placed in a solution pH=C for 24 hours, and the purity of impurity D also decreased, leading to chromatographic peak deformation (the data table is not presented due to space limitations).
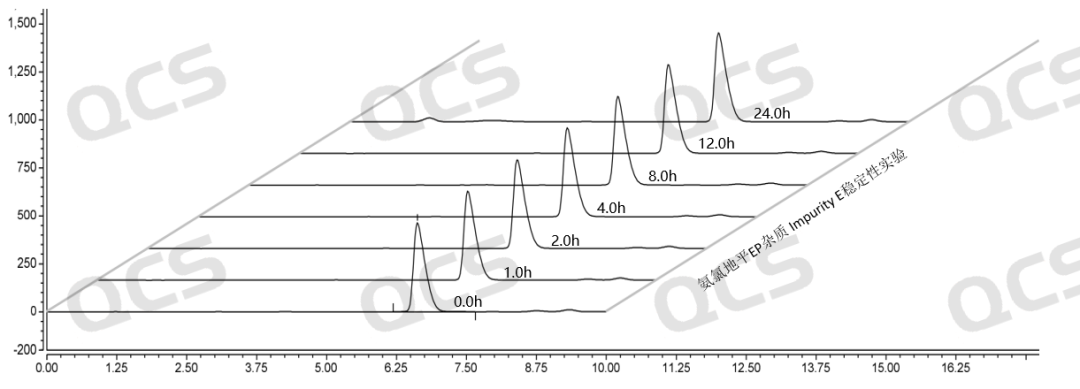
Figure 13: Summary of stability data for pH=A solution of EP impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205)
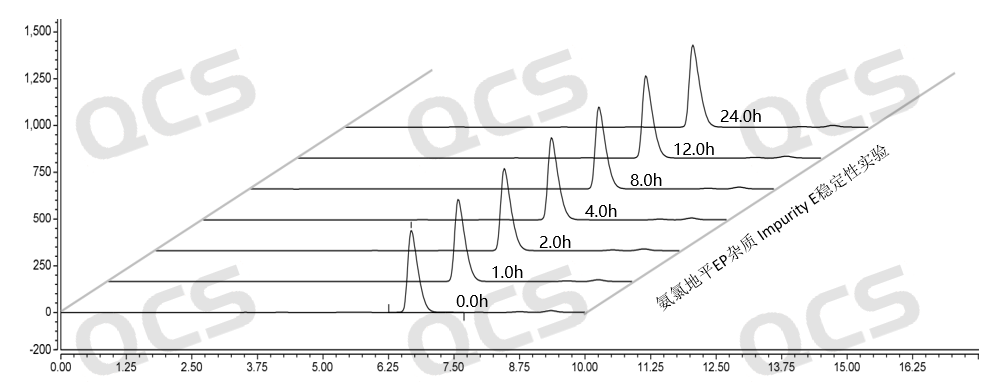
Figure 14: Summary of stability data for pH=B solution of EP Impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205)
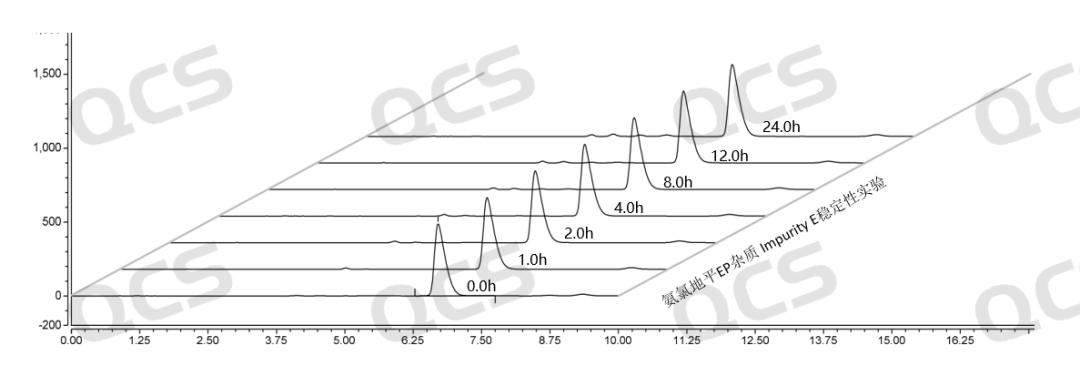
Figure 15: Summary of stability data for pH=C solution of EP impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205)
As can be seen from Figure 13-15, impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205) was placed in a solution of pH=A and B for 24 hours, and the peak area did not change much, indicating that the sample was relatively stable in solutions pH=A and B, and no degradation occurred. However, after impurity E was placed in the solution of pH=C for 24 hours, the peak area of the main peak gradually decreased with the extension of time. The results indicated that the impurity would be slowly degraded under pH=C, and the peak area of the main peak decreased by 6.27% within 24 hours. Therefore, during the storage and use of this product, it is also important to avoid contact with relevant acidic and alkaline substances, so as to avoid the degradation of the impurities and the deviation of the experimental results (Due to space limitations, the data table will not be presented).
05 Summary
In this research, the QCS Reference Material Research Center conducted stability studies on the impurities of Amlodipine series based on liquid chromatography positioning. The stability results of impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204), impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205) and Amlodipine Lactose Adduct impurity (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) are representative, providing data support for the storage and use of related impurities. Due to the space limitations of the article, the chromatographic localization and stability study data of other Amlodipine impurities are not fully displayed, if you are interested in the positioning and stability data of a certain impurity product, please contact the sales personnel you have contacted to obtain further research information.
01 Introduction
Today, we would like to share the data of Amlodipine-specific impurity stability research to provide data support for customers in the storage and use of related impurities. Judging from our current stability data, the product will indeed have a relatively obvious degradation under certain conditions, please refer to the research data below for details.
02 Introduction to Amlodipine-related projects
Amlodipine is a long-acting calcium antagonist that lowers blood pressure by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into heart and smooth muscle cells. It can be used for the treatment of hypertension and alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs, and can also be used for the treatment of coronary heart disease, such as chronic stable angina、vasospasm angina. Amlodipine-related impurities are our company's advantageous product items, in addition to the above-mentioned products, there are nearly 30 kinds of drug-related impurities, our company has more than 20 kinds of impurities in stock, and products information is shown in Figure 1 below:

Figure 1: The correspondence between the impurity codes included in the API and the standard and our company's impurity article numbers
The structural formula of inventory impurities is shown in Figure 2:

Figure 2: Structural formula of impurities included in API and QCS
03 Impurity localization studies
Our center conducted localization research on specific impurities first. By referring to the HPLC chromatographic conditions used in the《European Pharmacopoeia》 11.0 version 《AMODIPINE BESILATE》, conduct liquid chromatography localization studies on multiple impurities, including impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204) and impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205). The QCS R&D center conducted a series of studies on multiple impurity products and active pharmaceutical ingredients in stock, and calculated the relative retention time data of all impurity products. Our center has made appropriate adjustments to the EP conditions based on the existing chromatographic columns, and the measured relative retention time under these conditions is basically consistent with the data in the standard. It can be considered that the chromatographic results of the imported registration standard have been basically reproduced in this study. Due to space limitations, this article only extracts two impurity data for display (Figure 3-5) (If you have other data requirements, please contact the corresponding sales personnel).

Figure 3: Chromatogram of mixed injection of API and some impurities

Figure 4: Data related to Amlodipine API and two impurities in the EP Pharmacopoeia

Figure 5: Summary of tested data for Amlodipine and impurity E, F
04 Impurity stability research
In addition to qualitative research, many customers have significant concerns about how impurities are stored, used, whether the product is stable, and whether the data is reliable. Due to the particularity of impurity reference materials, there is a risk of spoilage during storage, transportation, and use of the product. So customers are particularly concerned about how to prepare, store, and use the reserve liquid.
In order to better answer customer questions, our center has conducted relevant stability research on specific impurities. The stability research of the solution was conducted on behalf of EP standard impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204), impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205), and USP standard Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211). This research will provide positive reference for the use of relevant reference materials, stability time, and reliability of sample results, in order to solve the confusion of product storage and use stability.
The experimental design for this experiment is as follows: Take the sample to be studied, place the sample in solutions with pH=A, B, and C three acid-base gradients, and test at 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 hours, respectively. Summarize the purity test results of the samples over time under different solution conditions, which can effectively reflect the stability trend of the samples under these conditions. The summary of the main peak area data for each detection point under various pH conditions is shown in Figures 6-9:

Figure 6: Summary of stability data for pH=A solution of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211)

Figure 7: Summary of stability data for pH=B solution of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211)

Figure 8: Summary of stability data for pH=C solution of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211)

Figure 9: Summary of main peak area data for stability testing of Amlodipine Lactose Adduct(QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) solution
From the above data, it can be seen that the Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) was left in solutions pH=A and B for 24 hours respectively, and no obvious impurity peaks were detected. At the same time, the main peak area did not change much, indicating that the sample was relatively stable in solutions pH=A and B and did not degrade. However, during the placement of a solution with pH=C, a continuous decrease in the area of the main peak and an increase in the number of impurity peaks can be monitored. Especially during the process from 0.0h to 4.0h, the purity of the product showed a significant decrease, indicating that the Amlodipine Lactose Adduct (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) is very unstable under pH=C solution conditions and will quickly degrade. Based on the above experimental data, customers are advised to pay special attention to the acid-base conditions when using this impurity to avoid abnormal detection results.
In addition, our center also conducted the same research and testing on impurities D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204) and E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205), the results are summarized in the following figure (10-12):

Figure 10: Summary of stability data for pH=A solution of EP Impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204)

Figure 11: Summary of stability data for pH=B solution of EP Impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204)

Figure 12: Summary of stability data for pH=C solution of EP Impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204)
As can be seen from Figure 10-12, impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204) was placed in a solution pH=C for 24 hours, and the purity of impurity D also decreased, leading to chromatographic peak deformation (the data table is not presented due to space limitations).

Figure 13: Summary of stability data for pH=A solution of EP impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205)

Figure 14: Summary of stability data for pH=B solution of EP Impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205)

Figure 15: Summary of stability data for pH=C solution of EP impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205)
As can be seen from Figure 13-15, impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205) was placed in a solution of pH=A and B for 24 hours, and the peak area did not change much, indicating that the sample was relatively stable in solutions pH=A and B, and no degradation occurred. However, after impurity E was placed in the solution of pH=C for 24 hours, the peak area of the main peak gradually decreased with the extension of time. The results indicated that the impurity would be slowly degraded under pH=C, and the peak area of the main peak decreased by 6.27% within 24 hours. Therefore, during the storage and use of this product, it is also important to avoid contact with relevant acidic and alkaline substances, so as to avoid the degradation of the impurities and the deviation of the experimental results (Due to space limitations, the data table will not be presented).
05 Summary
In this research, the QCS Reference Material Research Center conducted stability studies on the impurities of Amlodipine series based on liquid chromatography positioning. The stability results of impurity D (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131204), impurity E (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131205) and Amlodipine Lactose Adduct impurity (QCS Cat. No. RM-A131211) are representative, providing data support for the storage and use of related impurities. Due to the space limitations of the article, the chromatographic localization and stability study data of other Amlodipine impurities are not fully displayed, if you are interested in the positioning and stability data of a certain impurity product, please contact the sales personnel you have contacted to obtain further research information.
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号