Time:2025-07-18

Biotin, also known as vitamin H or coenzyme R, is a water-soluble vitamin and member of the B-complex family (vitamin B7). It serves as an essential component for vitamin C synthesis and plays a vital role in maintaining normal metabolic processes of fats and proteins. This nutrient is crucial for sustaining natural growth, healthy development, and optimal bodily functions. For those with thinning hair, biotin acts as a lifesaver—it not only helps prevent hair loss and reduces visible bald spots but also aids in combating the common premature graying seen in modern youth. Additionally, it plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin.
I. R&D Background
Since its first artificial synthesis in 1943, chemical researchers have pioneered over 70 years of advancements in biotin synthesis. Dozens of production routes have emerged in this field. During industrial manufacturing, biotin may develop various impurities influenced by factors like temperature, pH levels, and light exposure. The European Pharmacopoeia (EP) has conducted extensive research on biotin-related impurities. As one of our company's best-selling impurity products, we implemented the EP method to study six specific impurities (EP Impurities B, C, D, E, H, G) in biotin to enhance quality control. The EP-structured impurities are illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Structure of biotin EP impurity
2. HPLC method study
After conducting NMR and mass spectrometry qualitative analysis of biotin impurities, our company performed HPLC liquid chromatography analysis according to the EP standard method. Since the EP does not specify limit controls for all impurities, we divided the six biotin EP impurities into two groups for analysis. The first group included Impurity C and Impurity E, which were subject to limit control in the EP. The remaining four impurities (Impurities B, D, G, and H) formed the second group.
Group 1: The RRT of biotin impurity C specified in EP is 0.25, and the RRT of impurity E is 1.3. According to the standard method requirements of EP, our company used chromatography column with equivalent efficacy to the standard for analysis. The theoretical relative retention time of biotin and impurities B and E is shown in Figure 2, and the qualitative localization study results are shown in Figure 3 and Table 1.

Figure 2: EP standard theoretical relative retention time
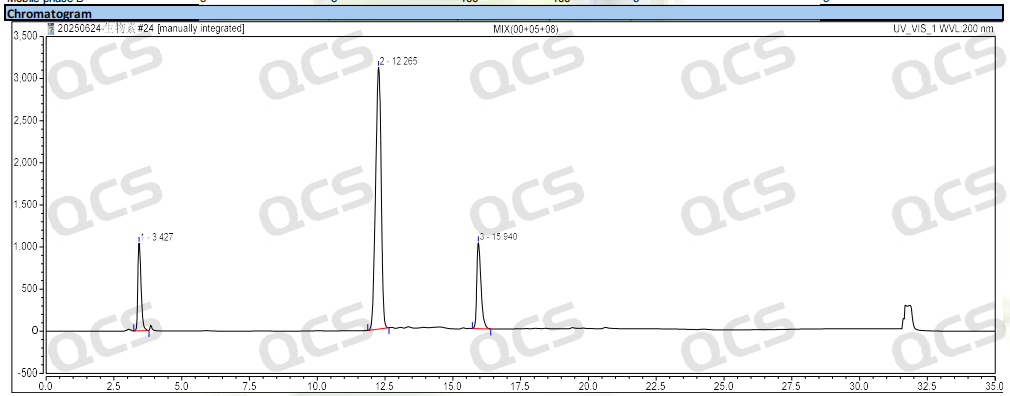
Figure 3: Chromatogram of biotin and impurity C and impurity E
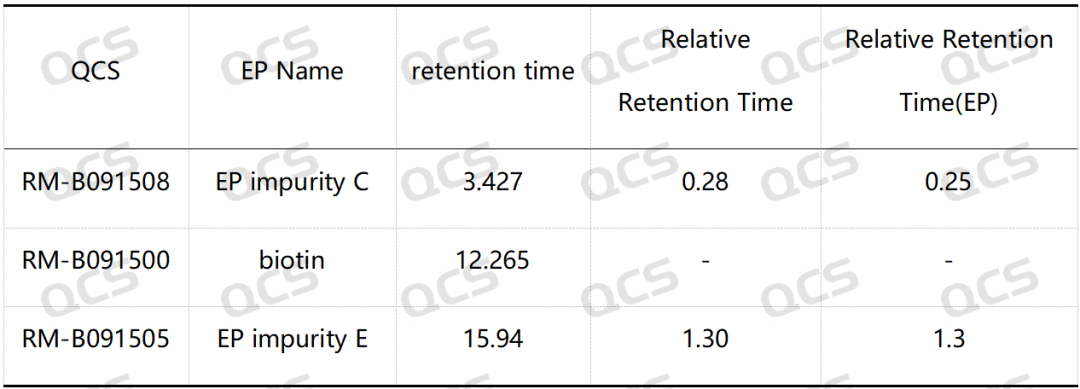
Table 1: Comparison of relative retention time (RRT) standard and measured values of biotin impurity C and impurity E
Group 2: According to the requirements of EP standard method, our company used chromatographic columns with equivalent efficacy to the standard for analysis. The qualitative localization results of biotin and impurities B, D, G and H are shown in Figure 4 and Table 2.
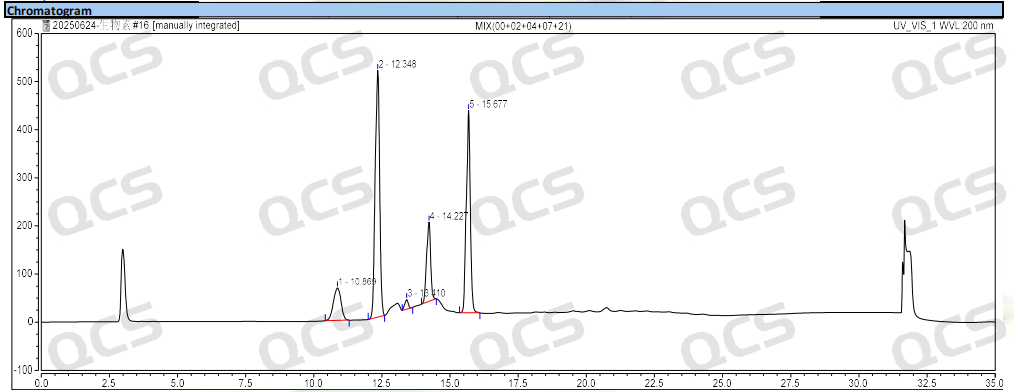
Figure 4: Chromatogram of biotin and impurities B, D, G and H
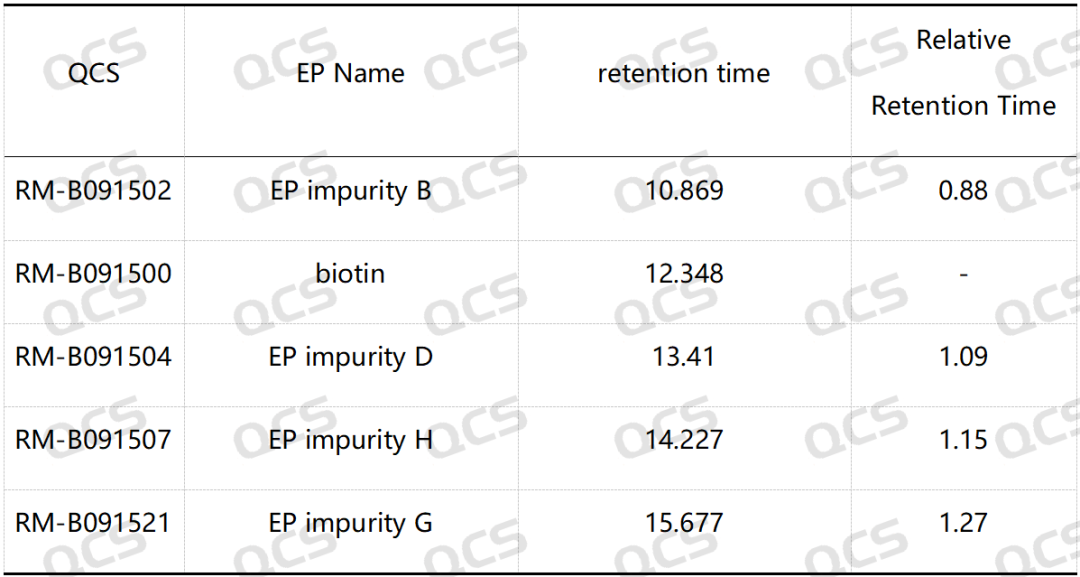
Table 2: Relative retention time (RRT) of biotin impurity B, impurity D, impurity G and impurity H
According to the above results, we can see that the relative retention time (RRT) of biotin EP impurity C and impurity E are within ±0.05 of the standard requirements. For biotin EP impurity B, impurity D, impurity G and impurity H, our company has also successfully realized the control and monitoring of them.
III. Summary
Through standard methods, our company can strictly control the quality of biotin impurities. In addition, biotin impurities are one of the most popular impurity series in our company. This series of impurities has complete chromatographic certificates, high purity, affordable prices, and can be customized. For more series of impurities, please consult your sales representative.



Biotin, also known as vitamin H or coenzyme R, is a water-soluble vitamin and member of the B-complex family (vitamin B7). It serves as an essential component for vitamin C synthesis and plays a vital role in maintaining normal metabolic processes of fats and proteins. This nutrient is crucial for sustaining natural growth, healthy development, and optimal bodily functions. For those with thinning hair, biotin acts as a lifesaver—it not only helps prevent hair loss and reduces visible bald spots but also aids in combating the common premature graying seen in modern youth. Additionally, it plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin.
I. R&D Background
Since its first artificial synthesis in 1943, chemical researchers have pioneered over 70 years of advancements in biotin synthesis. Dozens of production routes have emerged in this field. During industrial manufacturing, biotin may develop various impurities influenced by factors like temperature, pH levels, and light exposure. The European Pharmacopoeia (EP) has conducted extensive research on biotin-related impurities. As one of our company's best-selling impurity products, we implemented the EP method to study six specific impurities (EP Impurities B, C, D, E, H, G) in biotin to enhance quality control. The EP-structured impurities are illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Structure of biotin EP impurity
2. HPLC method study
After conducting NMR and mass spectrometry qualitative analysis of biotin impurities, our company performed HPLC liquid chromatography analysis according to the EP standard method. Since the EP does not specify limit controls for all impurities, we divided the six biotin EP impurities into two groups for analysis. The first group included Impurity C and Impurity E, which were subject to limit control in the EP. The remaining four impurities (Impurities B, D, G, and H) formed the second group.
Group 1: The RRT of biotin impurity C specified in EP is 0.25, and the RRT of impurity E is 1.3. According to the standard method requirements of EP, our company used chromatography column with equivalent efficacy to the standard for analysis. The theoretical relative retention time of biotin and impurities B and E is shown in Figure 2, and the qualitative localization study results are shown in Figure 3 and Table 1.

Figure 2: EP standard theoretical relative retention time

Figure 3: Chromatogram of biotin and impurity C and impurity E

Table 1: Comparison of relative retention time (RRT) standard and measured values of biotin impurity C and impurity E
Group 2: According to the requirements of EP standard method, our company used chromatographic columns with equivalent efficacy to the standard for analysis. The qualitative localization results of biotin and impurities B, D, G and H are shown in Figure 4 and Table 2.

Figure 4: Chromatogram of biotin and impurities B, D, G and H

Table 2: Relative retention time (RRT) of biotin impurity B, impurity D, impurity G and impurity H
According to the above results, we can see that the relative retention time (RRT) of biotin EP impurity C and impurity E are within ±0.05 of the standard requirements. For biotin EP impurity B, impurity D, impurity G and impurity H, our company has also successfully realized the control and monitoring of them.
III. Summary
Through standard methods, our company can strictly control the quality of biotin impurities. In addition, biotin impurities are one of the most popular impurity series in our company. This series of impurities has complete chromatographic certificates, high purity, affordable prices, and can be customized. For more series of impurities, please consult your sales representative.


Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号