Time:2025-04-29


Recently, our company received feedback from a customer: when using the European Pharmacopoeia (EP) method for related substance analysis, the liquid chromatography (HPLC) elution order of impurity B (Amlodipine EP Impurity B; CAS No:721958-72-1) and impurity G (Amlodipine EP Impurity G; CAS No:43067-01-2) did not match expectations. In response, our center has taken this matter very seriously and immediately initiated an investigation to ensure that product quality is controllable and analytical methods are reliable.
R&D Background: After-sales feedback meets difficulties
Customer feedback: The relative retention time of EP impurities B and G of Amlodipine does not match the standard. Customer specific test data: The customer used GL sciences ODS-3 chromatographic column (5um) and Agilent chromatographic column (Pursuit XRs), the peak is similar, and the RRT does not match the standard. See Figure 1 and Figure 2 for details:
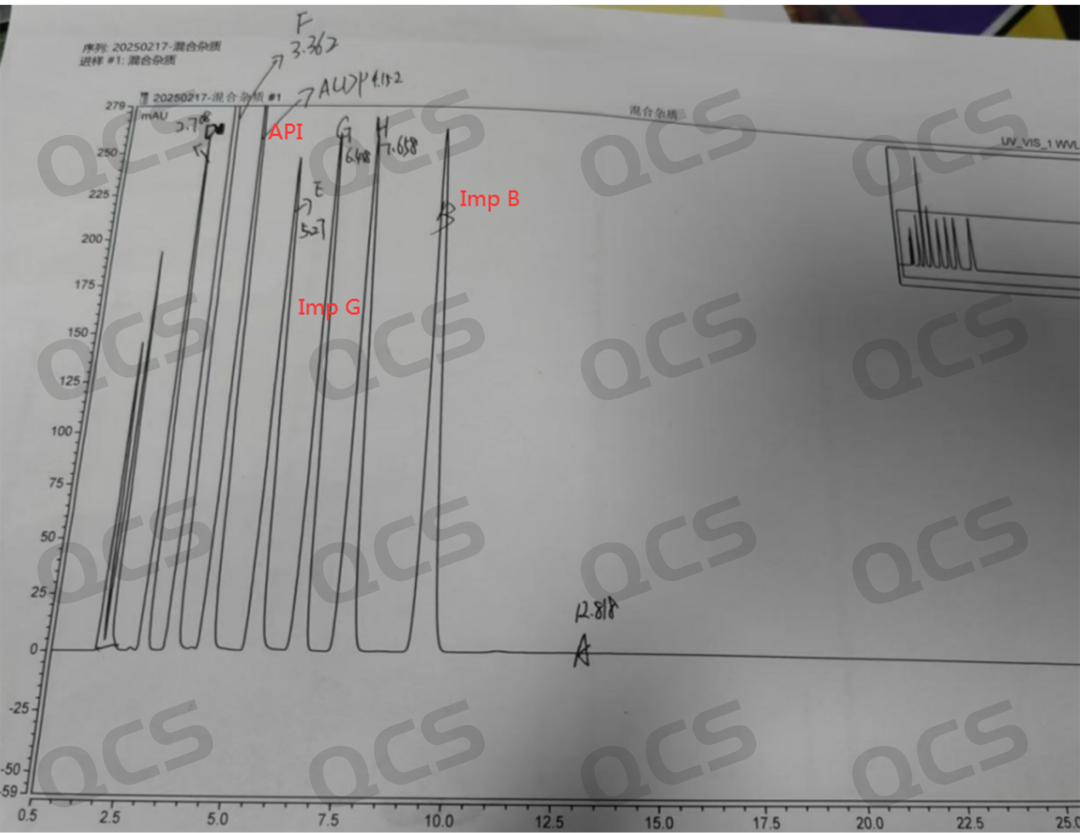
Figure 1: Sample mix of impurities provided by the customer
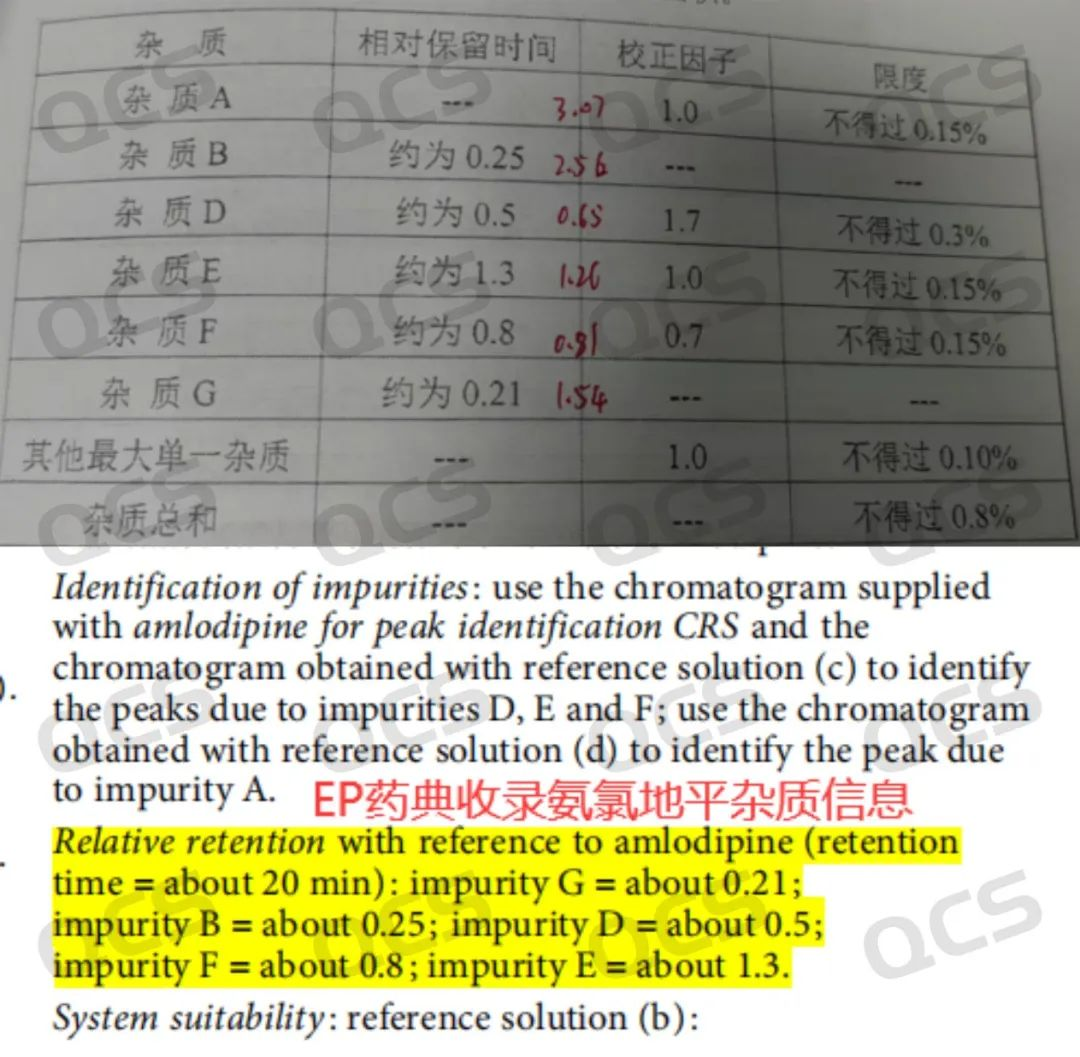
Figure 2: RRT data of impurity mix samples provided by customers and information included in EP pharmacopoeia standards
From Figures 1 and 2, it can be seen that impurities B and G differ significantly from the RRT recorded in the customer's standard. The API peak time is 4.152 minutes; impurity B peaks at 10.629; RRT=2.56 (the customer's standard is 0.25, consistent with the EP standard). Impurity G peaks at 6.458, with RRT=1.56 (the customer's standard is 0.21, consistent with the EP standard). Therefore, the customer reported to us that our product was incorrect. This feedback from after-sales service left us very puzzled. The series of impurities has been sold for over a decade, and theoretically, such an issue should not occur. Moreover, we have reviewed the corresponding batches of products, which have been delivered to more than ten customers, and none of them have reported similar issues. Thus, our center decided to investigate the problem from two directions.
The structural formula of amlodipine and amlodipine EP impurities is shown in Figure 3:
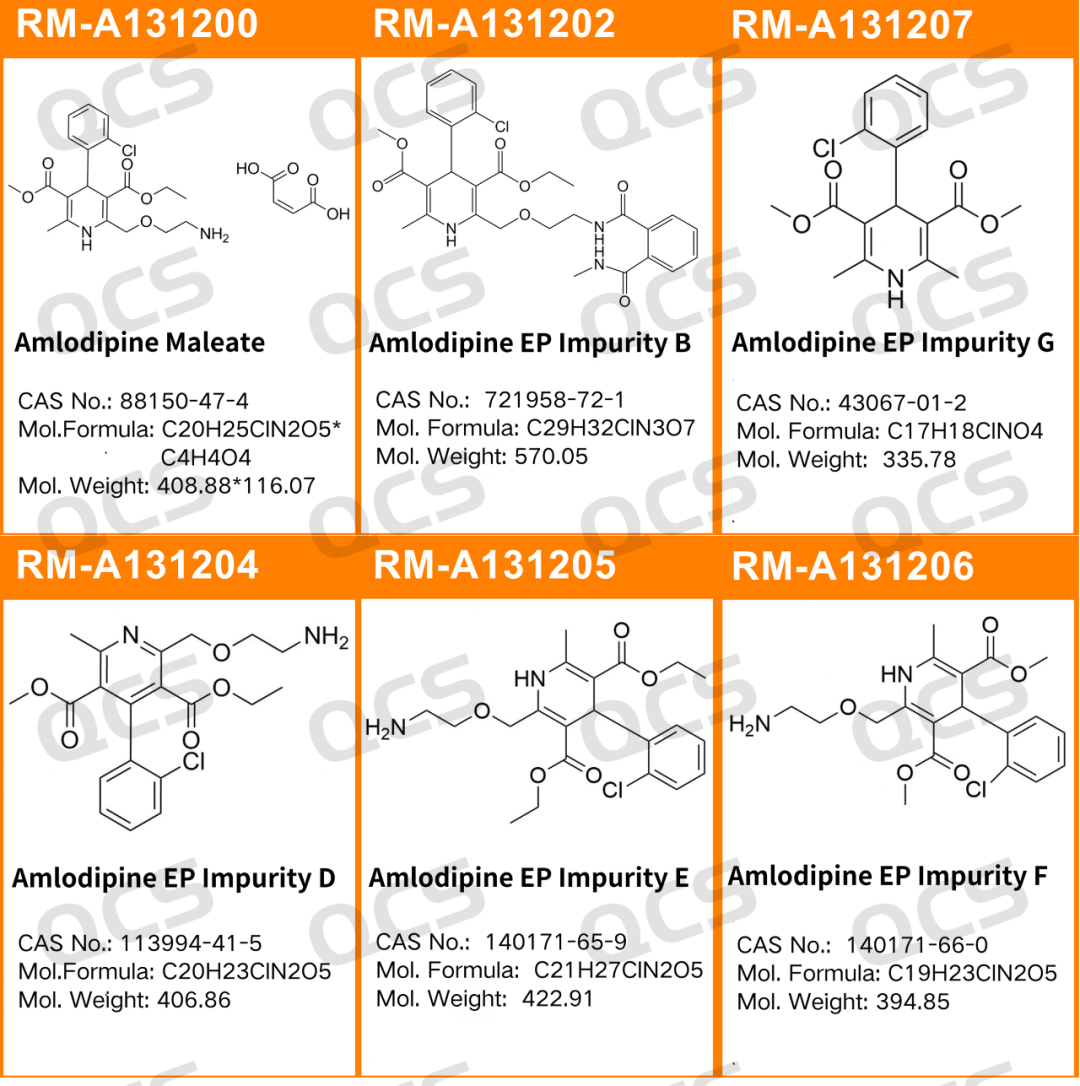
Figure 3: Structural information of amlodipine and EP impurities
Preliminary research and conclusions
Qualitative verification of impurities
First, the chemical structures of impurities B and G were verified. Based on mass spectrometry (MS) + nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis, it was confirmed that the chemical structures of these two impurities in the product are correct, ruling out any qualitative issues with the compounds themselves (Note: To accurately verify the product structure, our center also performed two-dimensional NMR spectra for the two impurities. Due to the simplicity of the product's structure, one-dimensional data is sufficient to prove the product structure, so we did not include the two-dimensional NMR data for B and G. Customers who need it can contact the sales representative privately to obtain it).
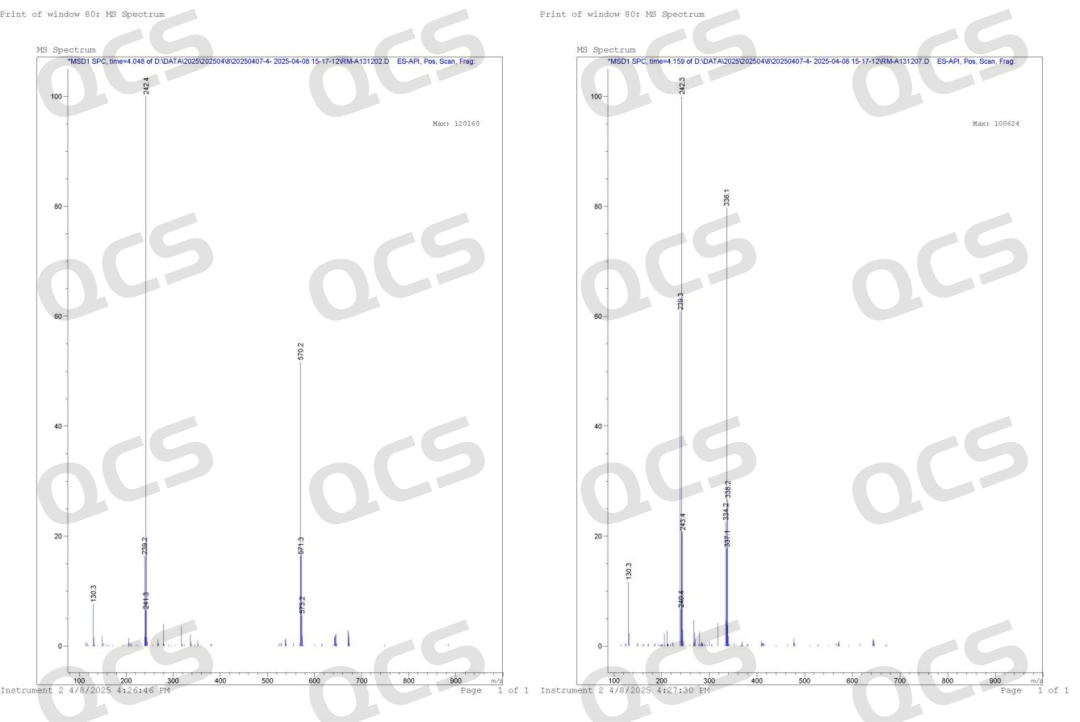
Figure 4: Mass spectra of EP impurities B (RM-A131202) and impurity G (RM-A131207) of amlodipine
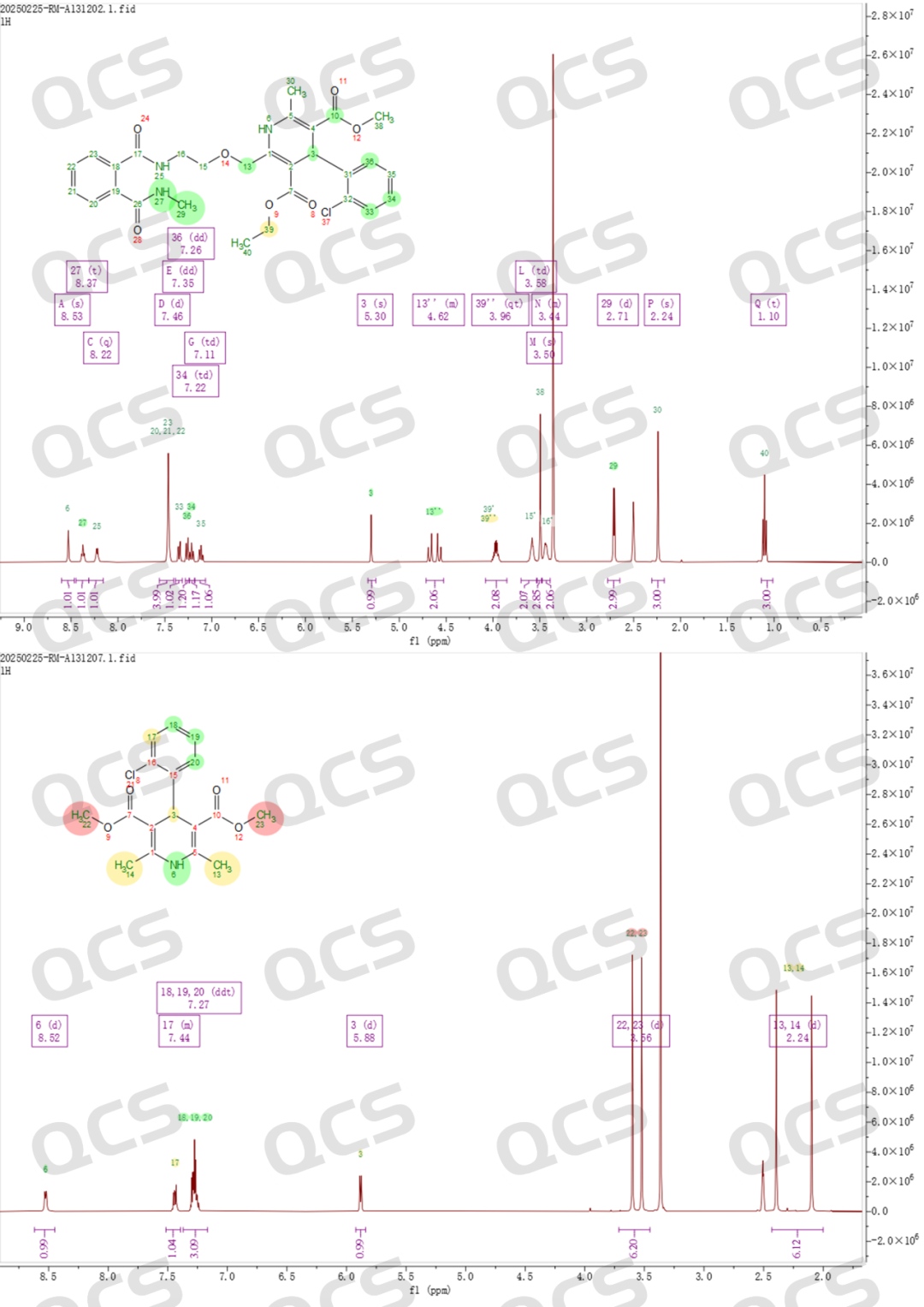
Figure 5: HNMR information and attribution of EP impurities B (RM-A131202) and impurity G (RM-A131207) of amlodipine
Screening of chromatographic conditions
From Figures 1 and 2, it is evident that the client's method involved some adjustments to the EP method (the RT of aldp in EP was 20 min). However, after communicating with the client, feedback indicated that apart from changing the chromatographic column, everything else remained consistent with the EP method. Therefore, we suspect that the data anomaly is most likely due to the chromatographic column. Subsequently, we strictly followed the parameters of the EP method (mobile phase composition, gradient program, column temperature, etc.) to retest impurities B, D, E, F, and G, and found that there indeed was an overlap in their retention times. To further expand the experimental scope, we selected five different brands of C18 chromatographic columns (YMC-Pack ODS 150*4.6 mm, Waters Xbridge 250*4.6 mm, Techer ODS-4 150*4.6 mm, Welch Xtimate-C18250*4.6 mm, Zorbax SB-C18250*4.6 mm) for comparison. The results showed significant differences in the peak order of impurities with different chromatographic columns (as shown in Figure 6).
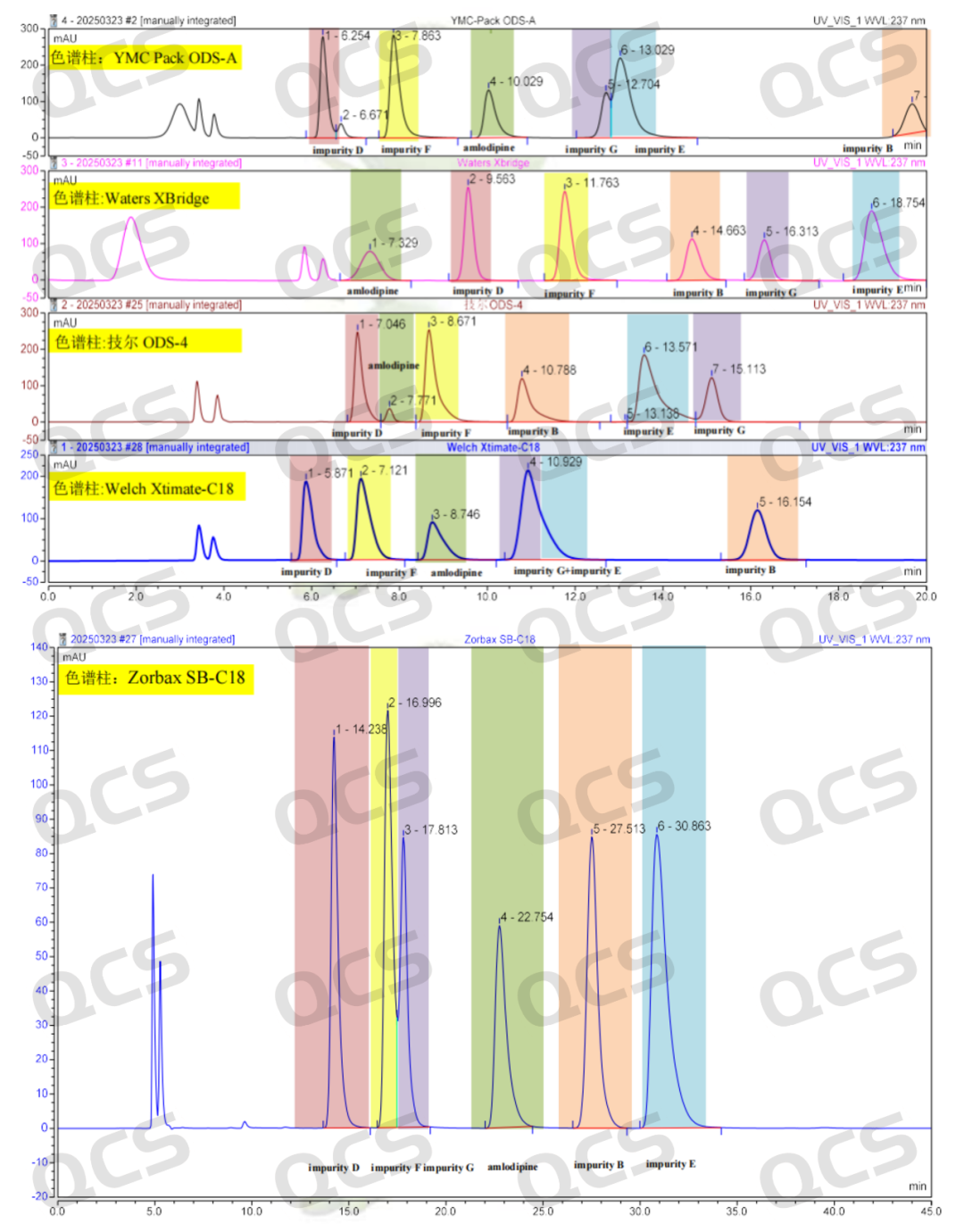
Figure 6: Liquid phase peak of impurities B, D, E, F and G in different chromatographic columns
Key findings: Chromatographic column selectivity difference
The performance of C18 chromatographic column is affected by many factors, including silica gel purity, bonding phase density, sealing process, pore size and so on. Amlodipine impurities B and G are structural analogs (both dihydropyridine derivatives), and their separation highly depends on the selectivity of the chromatographic column.
Differences in hydrophobicity and stereoselectivity: The coverage or spatial configuration of the bonded phase of different brands of chromatographic columns may change the interaction between impurity molecules and the stationary phase, resulting in retention shift.
Limitations of method specificity: EP methods are developed based on specific chromatographic columns, and their selectivity may not be fully transferred to other brand chromatographic columns.
4.
Through our verification data, we gave the customer a feedback. The core of the abnormal data was in the chromatographic column. Later, the customer strictly followed the chromatographic column (Waters Spherisorb ODS1,250x4.6mm, 5μm) included in the standard for testing, and the data could be matched with the standard. This after-sales problem was satisfactorily solved.
Solutions and suggestions for the detection of amlodipine products:
1. Strictly follow the EP recommended chromatographic column
The experiment confirmed that when the EP designated brand chromatographic column was not used, the elution order of impurities B and G was inconsistent with the pharmacopoeia. It is recommended that customers prioritize the use of EP recommended chromatographic column in the test to ensure the comparability and compliance of the results.
2. Verification of system applicability during method transfer
If the chromatographic column needs to be replaced, the system suitability test (SST) must be carried out again, focusing on the separation of impurity B and G (which should meet the EP requirements) and the matching of the elution order and retention time.
3.Technical communication and support
In response to customer questions, we can provide impurity reference and EP chromatographic column information to assist in optimizing separation conditions and ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Summary
The issue of peak sequence in the detection of amlodipine impurities is essentially due to differences in the selectivity of chromatographic columns. When developing pharmacopoeia methods, specific column selection parameters have been optimized. Therefore, strictly adhering to the recommended conditions in the pharmacopoeia is crucial for method reproducibility. We recommend that users thoroughly evaluate separation performance when selecting alternative columns and contact our technical support team if necessary.




Recently, our company received feedback from a customer: when using the European Pharmacopoeia (EP) method for related substance analysis, the liquid chromatography (HPLC) elution order of impurity B (Amlodipine EP Impurity B; CAS No:721958-72-1) and impurity G (Amlodipine EP Impurity G; CAS No:43067-01-2) did not match expectations. In response, our center has taken this matter very seriously and immediately initiated an investigation to ensure that product quality is controllable and analytical methods are reliable.
R&D Background: After-sales feedback meets difficulties
Customer feedback: The relative retention time of EP impurities B and G of Amlodipine does not match the standard. Customer specific test data: The customer used GL sciences ODS-3 chromatographic column (5um) and Agilent chromatographic column (Pursuit XRs), the peak is similar, and the RRT does not match the standard. See Figure 1 and Figure 2 for details:

Figure 1: Sample mix of impurities provided by the customer

Figure 2: RRT data of impurity mix samples provided by customers and information included in EP pharmacopoeia standards
From Figures 1 and 2, it can be seen that impurities B and G differ significantly from the RRT recorded in the customer's standard. The API peak time is 4.152 minutes; impurity B peaks at 10.629; RRT=2.56 (the customer's standard is 0.25, consistent with the EP standard). Impurity G peaks at 6.458, with RRT=1.56 (the customer's standard is 0.21, consistent with the EP standard). Therefore, the customer reported to us that our product was incorrect. This feedback from after-sales service left us very puzzled. The series of impurities has been sold for over a decade, and theoretically, such an issue should not occur. Moreover, we have reviewed the corresponding batches of products, which have been delivered to more than ten customers, and none of them have reported similar issues. Thus, our center decided to investigate the problem from two directions.
The structural formula of amlodipine and amlodipine EP impurities is shown in Figure 3:

Figure 3: Structural information of amlodipine and EP impurities
Preliminary research and conclusions
Qualitative verification of impurities
First, the chemical structures of impurities B and G were verified. Based on mass spectrometry (MS) + nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis, it was confirmed that the chemical structures of these two impurities in the product are correct, ruling out any qualitative issues with the compounds themselves (Note: To accurately verify the product structure, our center also performed two-dimensional NMR spectra for the two impurities. Due to the simplicity of the product's structure, one-dimensional data is sufficient to prove the product structure, so we did not include the two-dimensional NMR data for B and G. Customers who need it can contact the sales representative privately to obtain it).

Figure 4: Mass spectra of EP impurities B (RM-A131202) and impurity G (RM-A131207) of amlodipine

Figure 5: HNMR information and attribution of EP impurities B (RM-A131202) and impurity G (RM-A131207) of amlodipine
Screening of chromatographic conditions
From Figures 1 and 2, it is evident that the client's method involved some adjustments to the EP method (the RT of aldp in EP was 20 min). However, after communicating with the client, feedback indicated that apart from changing the chromatographic column, everything else remained consistent with the EP method. Therefore, we suspect that the data anomaly is most likely due to the chromatographic column. Subsequently, we strictly followed the parameters of the EP method (mobile phase composition, gradient program, column temperature, etc.) to retest impurities B, D, E, F, and G, and found that there indeed was an overlap in their retention times. To further expand the experimental scope, we selected five different brands of C18 chromatographic columns (YMC-Pack ODS 150*4.6 mm, Waters Xbridge 250*4.6 mm, Techer ODS-4 150*4.6 mm, Welch Xtimate-C18250*4.6 mm, Zorbax SB-C18250*4.6 mm) for comparison. The results showed significant differences in the peak order of impurities with different chromatographic columns (as shown in Figure 6).

Figure 6: Liquid phase peak of impurities B, D, E, F and G in different chromatographic columns
Key findings: Chromatographic column selectivity difference
The performance of C18 chromatographic column is affected by many factors, including silica gel purity, bonding phase density, sealing process, pore size and so on. Amlodipine impurities B and G are structural analogs (both dihydropyridine derivatives), and their separation highly depends on the selectivity of the chromatographic column.
Differences in hydrophobicity and stereoselectivity: The coverage or spatial configuration of the bonded phase of different brands of chromatographic columns may change the interaction between impurity molecules and the stationary phase, resulting in retention shift.
Limitations of method specificity: EP methods are developed based on specific chromatographic columns, and their selectivity may not be fully transferred to other brand chromatographic columns.
4.
Through our verification data, we gave the customer a feedback. The core of the abnormal data was in the chromatographic column. Later, the customer strictly followed the chromatographic column (Waters Spherisorb ODS1,250x4.6mm, 5μm) included in the standard for testing, and the data could be matched with the standard. This after-sales problem was satisfactorily solved.
Solutions and suggestions for the detection of amlodipine products:
1. Strictly follow the EP recommended chromatographic column
The experiment confirmed that when the EP designated brand chromatographic column was not used, the elution order of impurities B and G was inconsistent with the pharmacopoeia. It is recommended that customers prioritize the use of EP recommended chromatographic column in the test to ensure the comparability and compliance of the results.
2. Verification of system applicability during method transfer
If the chromatographic column needs to be replaced, the system suitability test (SST) must be carried out again, focusing on the separation of impurity B and G (which should meet the EP requirements) and the matching of the elution order and retention time.
3.Technical communication and support
In response to customer questions, we can provide impurity reference and EP chromatographic column information to assist in optimizing separation conditions and ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Summary
The issue of peak sequence in the detection of amlodipine impurities is essentially due to differences in the selectivity of chromatographic columns. When developing pharmacopoeia methods, specific column selection parameters have been optimized. Therefore, strictly adhering to the recommended conditions in the pharmacopoeia is crucial for method reproducibility. We recommend that users thoroughly evaluate separation performance when selecting alternative columns and contact our technical support team if necessary.


Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号