Time:2025-01-02
INTRODUCTION
In view of the fact that we have received multiple reports recently about N-nitrosamine impurities showing double peaks, customers have requested a relatively professional or official explanation. In fact, in a previous article titled "Sharing | NTTP Impurity of Sitagliptin, All Your Doubts about NMR Are Here!", we analyzed some specific manifestations of the nitrosamine structure in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. As mentioned above, due to the fact that the N-N bond has the property of a partial double bond, when the substituents on both sides of the N atom to which the nitrosamine is attached are different, there will be an energy difference between the Z/E isomers (the conformations of B1-B2 in the figure below). Since NMR is a rapid detection technique that can detect the object to be measured on a time scale of milliseconds to seconds, such a rapid time scale can distinguish between many pairs of objects to be measured that can be rapidly converted.
However, the relatively high price of the NMR spectrometer has led to the fact that the use of this equipment is not as widespread as that of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography (GC). So, what are the results of the analysis of N-nitrosamine impurities using the more commonly used chromatographic analysis methods? Will different conformational isomers of nitrosamines produce different chromatographic response signals?
In fact, the answer is yes: under certain chromatographic conditions, the conversion rate between the two conformations of nitrosamines will decrease, and even a high-purity nitrosamine sample will show two peaks in the chromatogram.
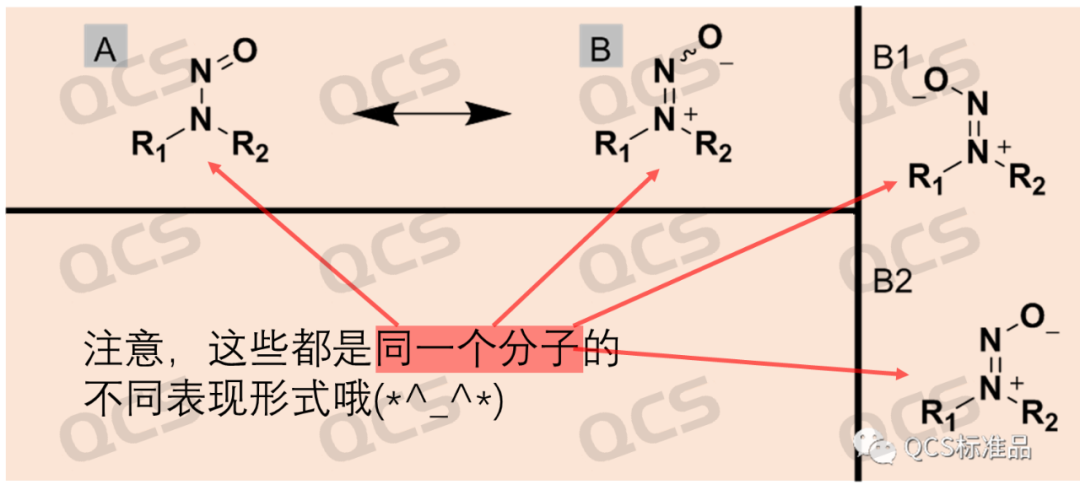
Figure 1: Example of the conformational differences in the nitrosamines
Among the hundreds of nitrosamine impurities produced by the QCS Reference Material R & D Center, the results of double peaks in liquid chromatography were shown. The differences in the conformational isomers of these molecules are relatively obvious, and the time required for conformational conversion is relatively long. Different conformational isomers can be well separated in HPLC, and the liquid chromatography results show double peaks. Through LC - MS tandem, the mass spectrometry identification of the signals of the two liquid chromatography peaks was carried out, and it was found that the mass spectrometry results of the two peaks were completely consistent.
CASE ANALYSIS
For example, Enalaprilat is a drug with a secondary amine structure within the molecule. The nitrosamine impurity of this drug will show two peaks in chromatography. This article will take this product as an example to share the results of nitrosamine conformational isomers in liquid chromatography.
After our center completed the directional synthesis of the nitrosamine impurity of Enalaprilat, it was found that this product could show distinct double peaks under certain chromatographic conditions (Figure 2, with retention times of 17 minutes and 20 minutes respectively). Mass spectrometry identification was carried out on the double peaks, and it was confirmed that their compositions were the same (Figure 3). Finally, combined with the nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy data (Figure 4), it could be confirmed that the sample only contained the structure of Enalaprilat nitrosamine and had a high purity. Through analysis, it was found that: the structural differences on both sides of the secondary amine within the molecule were relatively large, and the energy differences between the syn/anti (B1/B2) conformational isomers of the nitrosamine were significant, and the conversion rate was low. Therefore, different conformational isomers could be effectively separated under these chromatographic conditions, resulting in double peaks. The relevant data are shown in the figure below (However, it should be noted that these two peaks are still the same compound, and the two peaks can interconvert, as shown in the NMR result in Figure 4).
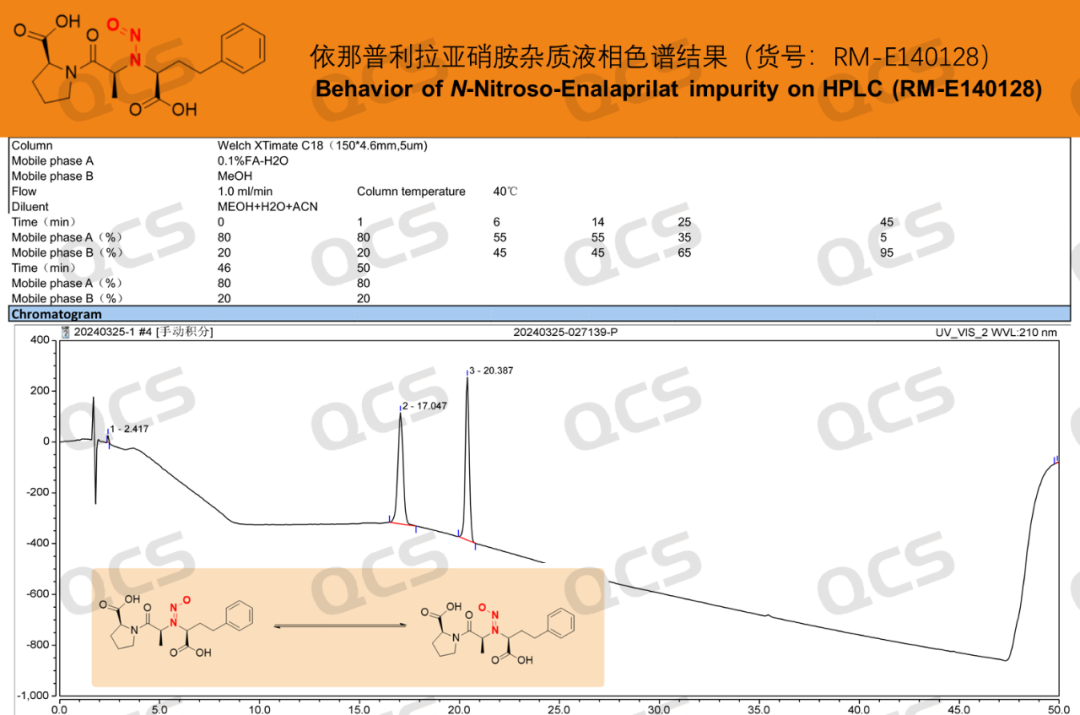
Figure 2: Liquid chromatography results of enalapril-nitrosamine impurities
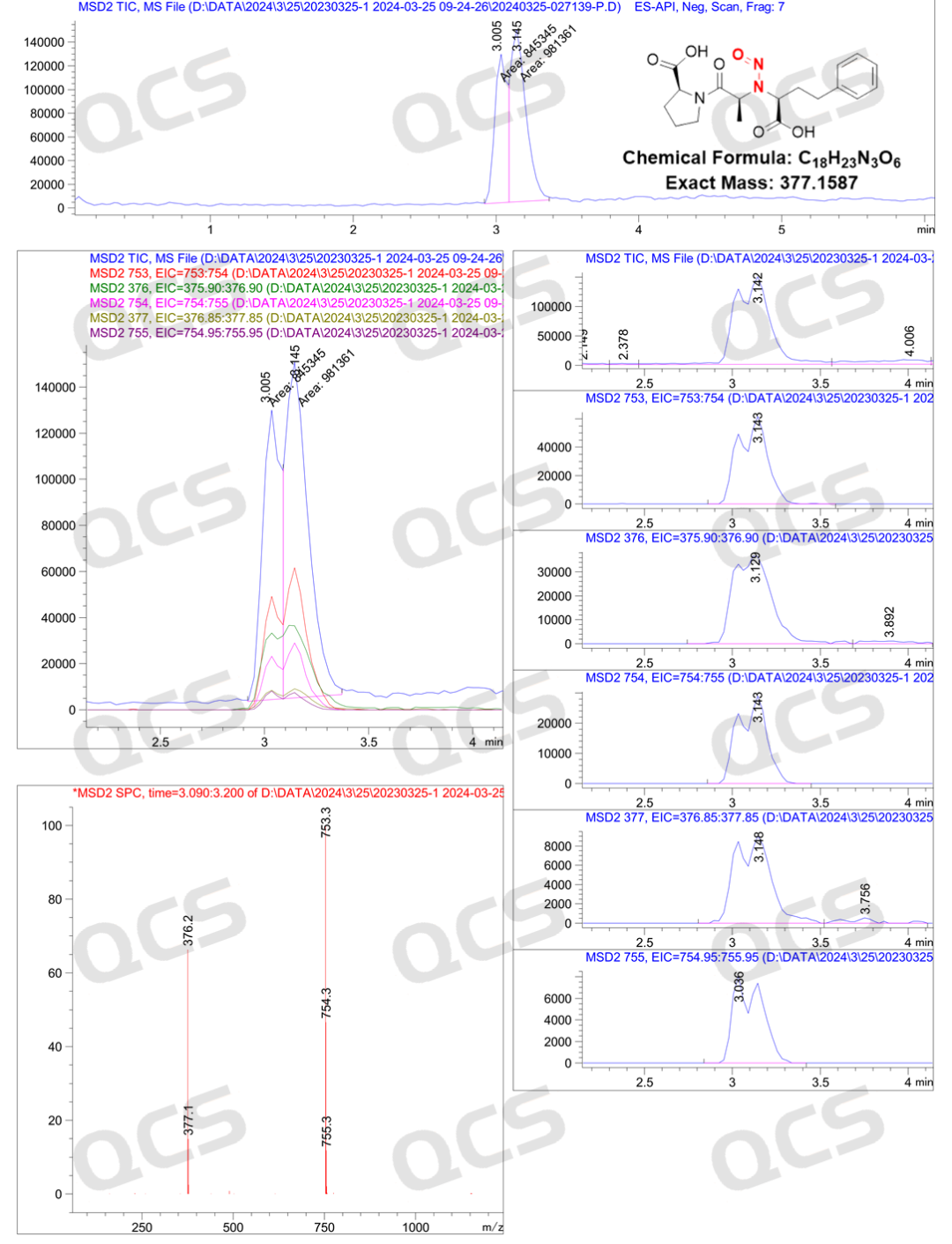
Figure 3: Mass spectrum results of enalapril-nitrosamine impurities
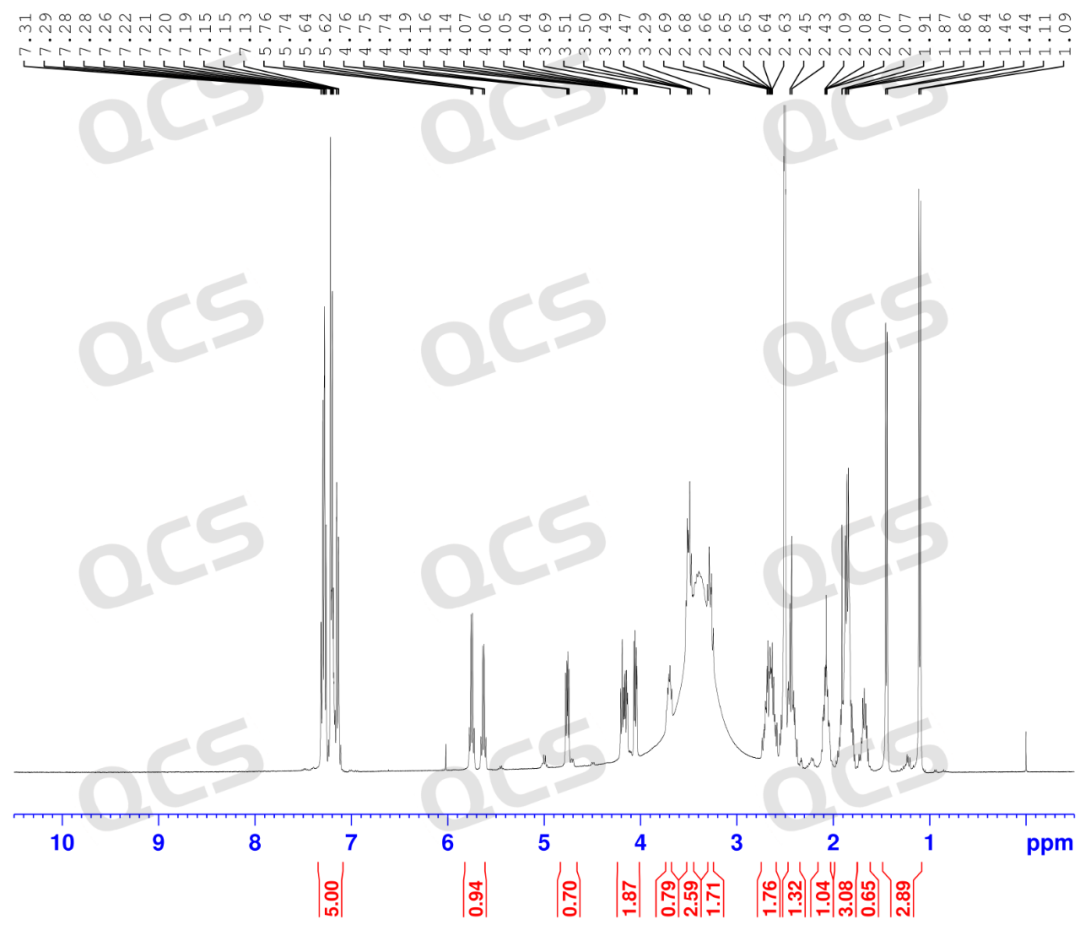
Figure 4: NMR hydrogen spectrum results of enalapril-nitrosamine impurity
Literature data
Through literature research, we found that the double - peak phenomenon of nitrosamines in chromatographic studies is a common one, and this issue has been mentioned in multiple research papers and official institutional documents. For example, a study published by F. Berthou et al. in France in 1996 (Journal of Chromatography A 1996, 727 (1), 83, Figure 5) showed that under optimized chromatographic conditions, asymmetric nitrosamine impurities could be separated, changing from a single peak to double peaks. Moreover, in the "USP General Chapter 1469 Nitrosamine Impurities" of the United States Pharmacopeia, it is clearly stated that the asymmetric nitrosamines NMBA and NEIPA may exhibit double peaks under the listed conditions (Figure 6).
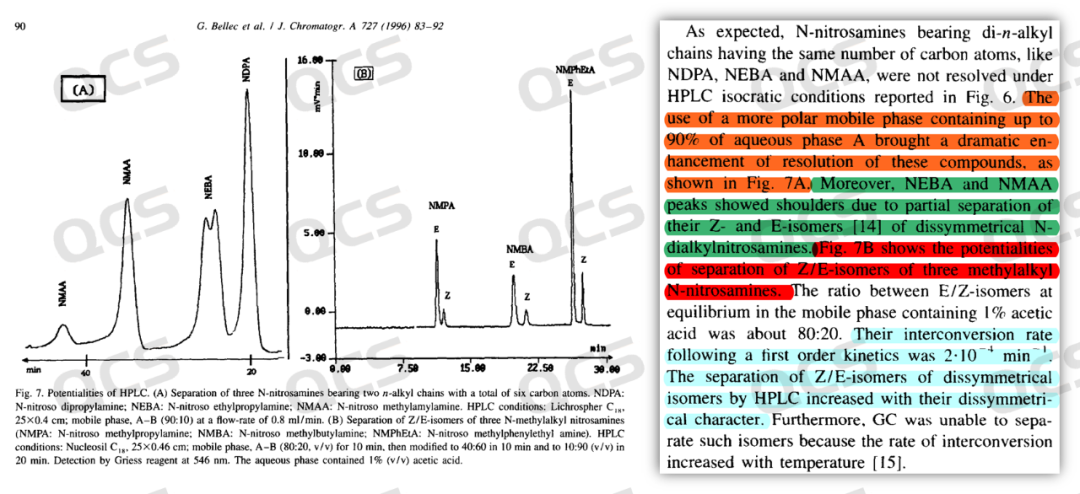
Figure 5: Case literature for the separation of the different conformations of the nitrosamines by liquid chromatography
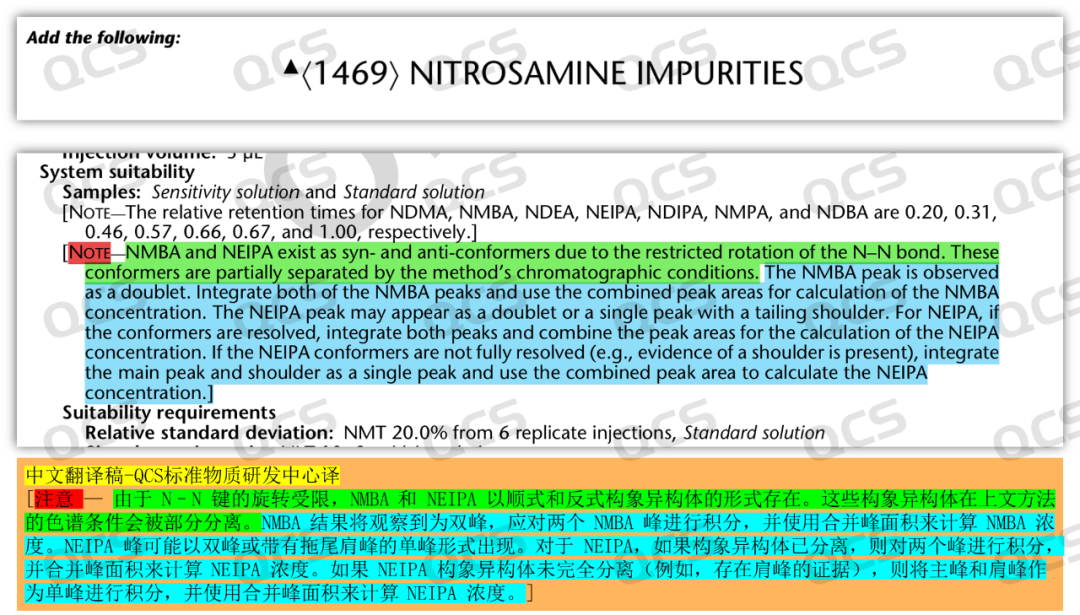
Figure 6: USP General Rules 1469 Nitrosamine Impurities
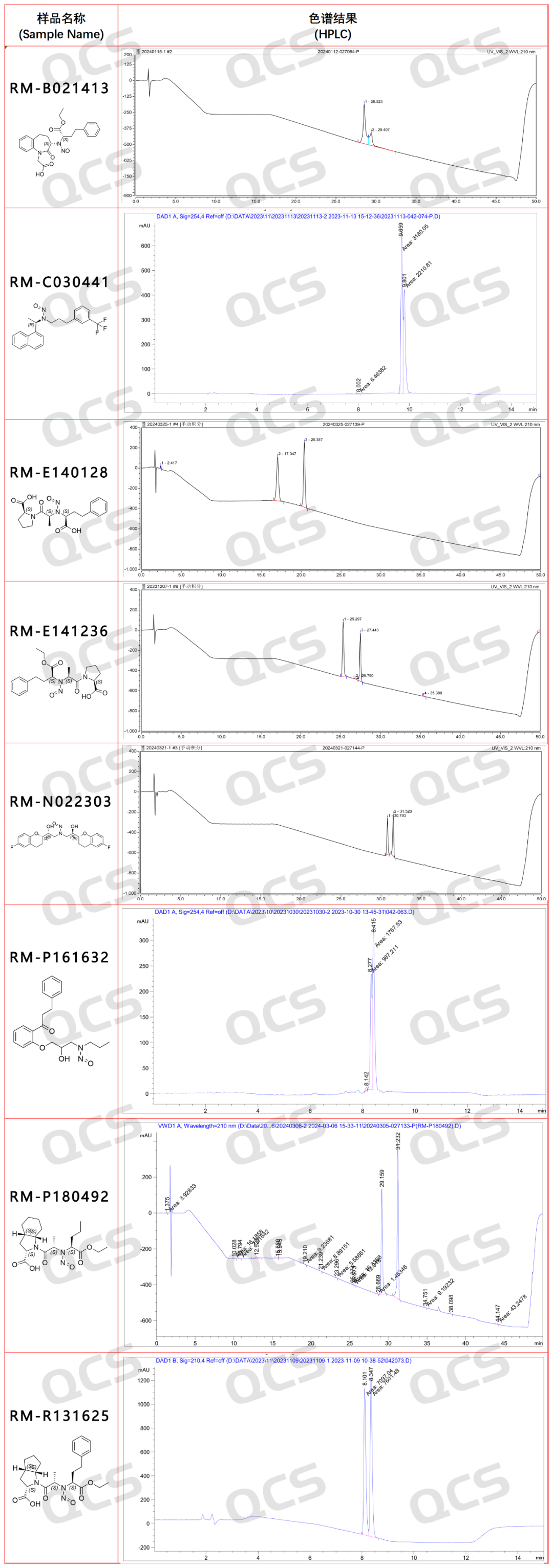
Finally, here is a data list of some nitrosamine cases from our center. These samples can all produce double peaks in liquid chromatography under specific conditions. The chromatographic results have all been verified and can be used with confidence. (Only some cases are extracted below. For detailed data, please contact the corresponding salesperson.)
APPENDIX
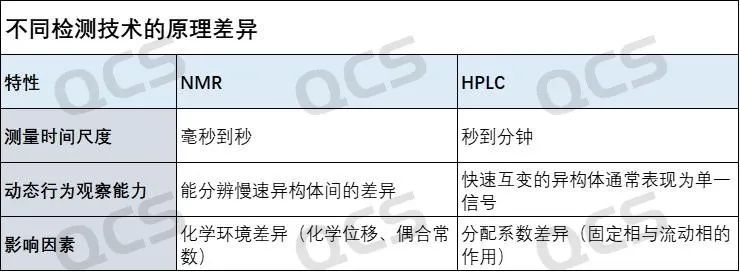
Regarding nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), they each have different focuses in chemical analysis. For pure nitrosamine samples, the measurement principles and dimensions of these two methods are different. The typical differences between the two measurement techniques are briefly summarized in the following table for reference.

INTRODUCTION
In view of the fact that we have received multiple reports recently about N-nitrosamine impurities showing double peaks, customers have requested a relatively professional or official explanation. In fact, in a previous article titled "Sharing | NTTP Impurity of Sitagliptin, All Your Doubts about NMR Are Here!", we analyzed some specific manifestations of the nitrosamine structure in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. As mentioned above, due to the fact that the N-N bond has the property of a partial double bond, when the substituents on both sides of the N atom to which the nitrosamine is attached are different, there will be an energy difference between the Z/E isomers (the conformations of B1-B2 in the figure below). Since NMR is a rapid detection technique that can detect the object to be measured on a time scale of milliseconds to seconds, such a rapid time scale can distinguish between many pairs of objects to be measured that can be rapidly converted.
However, the relatively high price of the NMR spectrometer has led to the fact that the use of this equipment is not as widespread as that of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography (GC). So, what are the results of the analysis of N-nitrosamine impurities using the more commonly used chromatographic analysis methods? Will different conformational isomers of nitrosamines produce different chromatographic response signals?
In fact, the answer is yes: under certain chromatographic conditions, the conversion rate between the two conformations of nitrosamines will decrease, and even a high-purity nitrosamine sample will show two peaks in the chromatogram.

Figure 1: Example of the conformational differences in the nitrosamines
Among the hundreds of nitrosamine impurities produced by the QCS Reference Material R & D Center, the results of double peaks in liquid chromatography were shown. The differences in the conformational isomers of these molecules are relatively obvious, and the time required for conformational conversion is relatively long. Different conformational isomers can be well separated in HPLC, and the liquid chromatography results show double peaks. Through LC - MS tandem, the mass spectrometry identification of the signals of the two liquid chromatography peaks was carried out, and it was found that the mass spectrometry results of the two peaks were completely consistent.
CASE ANALYSIS
For example, Enalaprilat is a drug with a secondary amine structure within the molecule. The nitrosamine impurity of this drug will show two peaks in chromatography. This article will take this product as an example to share the results of nitrosamine conformational isomers in liquid chromatography.
After our center completed the directional synthesis of the nitrosamine impurity of Enalaprilat, it was found that this product could show distinct double peaks under certain chromatographic conditions (Figure 2, with retention times of 17 minutes and 20 minutes respectively). Mass spectrometry identification was carried out on the double peaks, and it was confirmed that their compositions were the same (Figure 3). Finally, combined with the nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy data (Figure 4), it could be confirmed that the sample only contained the structure of Enalaprilat nitrosamine and had a high purity. Through analysis, it was found that: the structural differences on both sides of the secondary amine within the molecule were relatively large, and the energy differences between the syn/anti (B1/B2) conformational isomers of the nitrosamine were significant, and the conversion rate was low. Therefore, different conformational isomers could be effectively separated under these chromatographic conditions, resulting in double peaks. The relevant data are shown in the figure below (However, it should be noted that these two peaks are still the same compound, and the two peaks can interconvert, as shown in the NMR result in Figure 4).

Figure 2: Liquid chromatography results of enalapril-nitrosamine impurities

Figure 3: Mass spectrum results of enalapril-nitrosamine impurities

Figure 4: NMR hydrogen spectrum results of enalapril-nitrosamine impurity
Literature data
Through literature research, we found that the double - peak phenomenon of nitrosamines in chromatographic studies is a common one, and this issue has been mentioned in multiple research papers and official institutional documents. For example, a study published by F. Berthou et al. in France in 1996 (Journal of Chromatography A 1996, 727 (1), 83, Figure 5) showed that under optimized chromatographic conditions, asymmetric nitrosamine impurities could be separated, changing from a single peak to double peaks. Moreover, in the "USP General Chapter 1469 Nitrosamine Impurities" of the United States Pharmacopeia, it is clearly stated that the asymmetric nitrosamines NMBA and NEIPA may exhibit double peaks under the listed conditions (Figure 6).

Figure 5: Case literature for the separation of the different conformations of the nitrosamines by liquid chromatography

Figure 6: USP General Rules 1469 Nitrosamine Impurities
Finally, here is a data list of some nitrosamine cases from our center. These samples can all produce double peaks in liquid chromatography under specific conditions. The chromatographic results have all been verified and can be used with confidence. (Only some cases are extracted below. For detailed data, please contact the corresponding salesperson.)

APPENDIX
Regarding nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), they each have different focuses in chemical analysis. For pure nitrosamine samples, the measurement principles and dimensions of these two methods are different. The typical differences between the two measurement techniques are briefly summarized in the following table for reference.


Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号