Time:2022-12-08
Quotation: Quality is the lifeline of enterprises and brands. The Quality Control Solutions Ltd. (QCS) Standard Material Research and Development Center has consistently prioritized meticulous attention to detail in the advancement of the pharmaceutical industry, delivering precise and reliable standard products and services to our clients.
Taking betaprolol hydrochloride S-isomer (QCS item No.: RM-B050106) as an example, this paper outlines the content calibration process for products developed by the QCS R&D Center. Regarding the packaging, preparation, and calibration of chemical standards, QCS has obtained certification under the ISO9001:2015 quality management system, as illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1: ISO9001:2015 Quality Management System Certification for the QCS R&D Center
(Source: QCS R&D Center)
Betaprolol, a selective beta1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, was patented in 1975 and subsequently licensed for clinical use in 1983. To date, betaprolol remains the only selective β1-adrenergic receptor blocker utilized in ophthalmology. It exerts its therapeutic effects by selectively acting on β1 receptors, thereby achieving antihypertensive outcomes through the reduction of aqueous humor production and enhancement of aqueous humor outflow. Betaprolol is clinically indicated for the management of chronic open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and normal-tension glaucoma.
CAT Number: RM-B050106
Product Name: Betaxolol S-Isomer
Chemical Name: (S)-1-(4-(2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl)phenoxy)-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol hydrochloride
CAS Number: 116209-55-3
Molecular Formula: C18H29NO3*HCl
Molecular Weight: 307.43*36.46
The structural formula is presented in Figure 2.
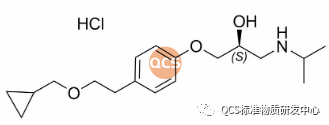
Figure 2: Structural Formula of the S-isomer of Betalolol
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
1. Identification Items
1.1 Mass Spectrometry (MS) Detection: The qualitative analysis of the sample was conducted using mass spectrometry and hydrogen NMR spectroscopy. The molecular formula of the S-isomer of betalolol in this sample is C18H29NO3, with an exact molecular weight of 307.2. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was employed for detection using an ESI ion source. The observed mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) was 308.5, corresponding to the [M+H]+ ion peak. These findings are consistent with the provided sample information. The mass spectrum and analytical data are presented in Figure 3.
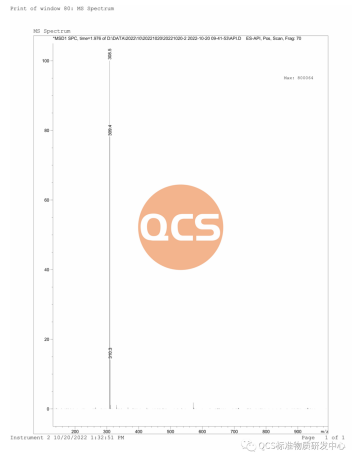
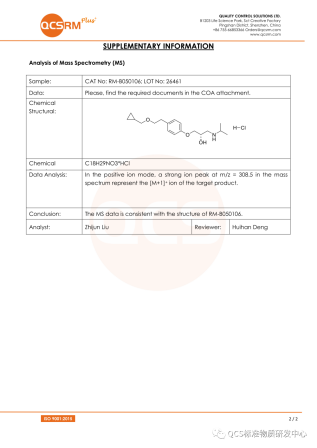
Figure 3: Mass Spectrometry Map and Analytical Data of the S-Isomer of Betaprolol
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
1.2 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (HNMR) Analysis: A second sample, weighing approximately 10 mg, was dissolved in deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6) for HNMR analysis. The integration of the proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectrum indicated a total of 30 protons in the sample. Specifically, the chemical shift range from 8.0 to 9.0 ppm exhibited two protons corresponding to amino and its hydrochloride signals. The aromatic ring protons were observed between 6.7 and 7.1 ppm, totaling four protons. A doublet at 5.7 ppm was attributed to the hydroxyl hydrogen. In the region from 2.7 to 4.2 ppm, ten protons were identified as CH groups attached to heteroatoms. For the CH2 signals, two protons appeared as a triplet near 2.6 ppm, corresponding to the aryl benzyl position. Six protons, appearing as two methyl (CH3) groups, were observed near 1.1 ppm. Lastly, five protons in the chemical shift range from 0.0 to 1.0 ppm were assigned to the cyclopropane structure.
The NMR spectral results are in agreement with the proposed structure of the product. The hydrogen NMR spectroscopic data and analysis are presented in Figure 4.

Figure 4: Betaprolol S-isomer HNMR Spectrum and Analytical Data
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
2. Purity Test Parameters
Approximately 20 mg of the sample was dissolved to prepare a test solution with a concentration of 1 mg/mL. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis revealed that the purity of the test solution was 99.66%. The detailed experimental conditions are outlined below.
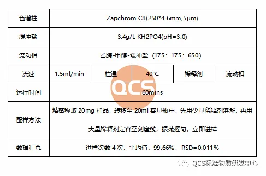
The liquid chromatogram is presented in Figure 5.
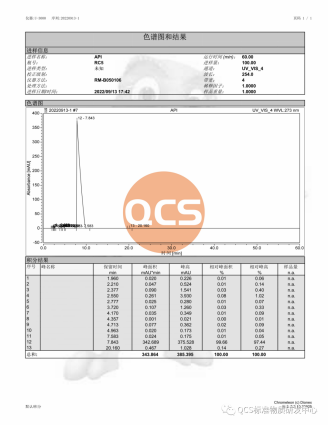
Figure 5: Liquid Chromatogram (Source: QCS R&D Center)
3. Solvent Residues
In accordance with the sample production and treatment procedures, potential residual solvents in the samples were analyzed. The detected solvent residues included methyl isobutyl ketone and isopropylamine. Quantification was performed using the external standard method, and the results are presented in Figure 6.
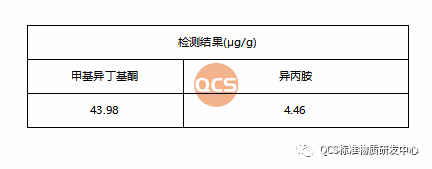
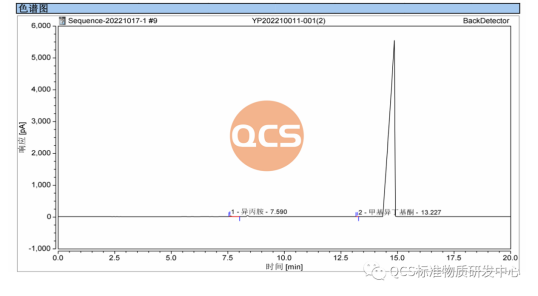
Figure 6: Chromatogram of Solvent Residue (Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
4. Determination of Incandescent Residue
The incandescent residue of the sample was determined in accordance with General Rule 0841 of Part IV of the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. A precisely weighed quantity of 1.0 g of the test substance was placed in a pre-weighed crucible. The crucible was then placed on an electric hot plate and gradually heated until complete carbonization occurred, followed by cooling. Approximately 1 mL of sulfuric acid was added to moisten the residue, which was subsequently heated at a low temperature until all sulfuric acid fumes were exhausted. The crucible was incinerated at 700 °C until complete ashing was achieved. After transferring the crucible to a desiccator and allowing it to cool, it was reweighed with precision. The crucible was then incinerated again at 700-800 °C until constant weight was reached. The final result indicated that the incandescent residue of the sample was 0.03%, as illustrated in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Drying Weight Loss Measurement Data (Source: QCS R&D Center)
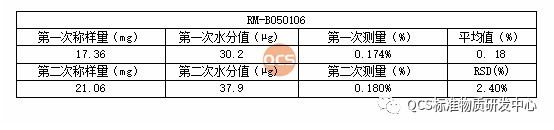
5. Moisture Measurement Procedures
The water content of the sample was determined using Callister coulometry. The results are presented as follows:
6. Sample Test Results
The comprehensive data for the aforementioned test items are as follows: Final Content = (1 - moisture - incandescent residue - residual solvent) * purity * 100%. The content of the current sample, based on this formula, is determined to be 99.45%.
The product test report is presented in Figure 8 below.

Figure 8: Analysis of S-isomer Content in Betalolol
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
If you ever need help with packaging, configuration, or content calibration, please don't hesitate to reach out to our sales representative. We're here to assist you!

Quotation: Quality is the lifeline of enterprises and brands. The Quality Control Solutions Ltd. (QCS) Standard Material Research and Development Center has consistently prioritized meticulous attention to detail in the advancement of the pharmaceutical industry, delivering precise and reliable standard products and services to our clients.
Taking betaprolol hydrochloride S-isomer (QCS item No.: RM-B050106) as an example, this paper outlines the content calibration process for products developed by the QCS R&D Center. Regarding the packaging, preparation, and calibration of chemical standards, QCS has obtained certification under the ISO9001:2015 quality management system, as illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1: ISO9001:2015 Quality Management System Certification for the QCS R&D Center
(Source: QCS R&D Center)
Betaprolol, a selective beta1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, was patented in 1975 and subsequently licensed for clinical use in 1983. To date, betaprolol remains the only selective β1-adrenergic receptor blocker utilized in ophthalmology. It exerts its therapeutic effects by selectively acting on β1 receptors, thereby achieving antihypertensive outcomes through the reduction of aqueous humor production and enhancement of aqueous humor outflow. Betaprolol is clinically indicated for the management of chronic open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and normal-tension glaucoma.
CAT Number: RM-B050106
Product Name: Betaxolol S-Isomer
Chemical Name: (S)-1-(4-(2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl)phenoxy)-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol hydrochloride
CAS Number: 116209-55-3
Molecular Formula: C18H29NO3*HCl
Molecular Weight: 307.43*36.46
The structural formula is presented in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Structural Formula of the S-isomer of Betalolol
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
1. Identification Items
1.1 Mass Spectrometry (MS) Detection: The qualitative analysis of the sample was conducted using mass spectrometry and hydrogen NMR spectroscopy. The molecular formula of the S-isomer of betalolol in this sample is C18H29NO3, with an exact molecular weight of 307.2. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was employed for detection using an ESI ion source. The observed mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) was 308.5, corresponding to the [M+H]+ ion peak. These findings are consistent with the provided sample information. The mass spectrum and analytical data are presented in Figure 3.


Figure 3: Mass Spectrometry Map and Analytical Data of the S-Isomer of Betaprolol
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
1.2 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (HNMR) Analysis: A second sample, weighing approximately 10 mg, was dissolved in deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6) for HNMR analysis. The integration of the proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectrum indicated a total of 30 protons in the sample. Specifically, the chemical shift range from 8.0 to 9.0 ppm exhibited two protons corresponding to amino and its hydrochloride signals. The aromatic ring protons were observed between 6.7 and 7.1 ppm, totaling four protons. A doublet at 5.7 ppm was attributed to the hydroxyl hydrogen. In the region from 2.7 to 4.2 ppm, ten protons were identified as CH groups attached to heteroatoms. For the CH2 signals, two protons appeared as a triplet near 2.6 ppm, corresponding to the aryl benzyl position. Six protons, appearing as two methyl (CH3) groups, were observed near 1.1 ppm. Lastly, five protons in the chemical shift range from 0.0 to 1.0 ppm were assigned to the cyclopropane structure.
The NMR spectral results are in agreement with the proposed structure of the product. The hydrogen NMR spectroscopic data and analysis are presented in Figure 4.


Figure 4: Betaprolol S-isomer HNMR Spectrum and Analytical Data
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
2. Purity Test Parameters
Approximately 20 mg of the sample was dissolved to prepare a test solution with a concentration of 1 mg/mL. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis revealed that the purity of the test solution was 99.66%. The detailed experimental conditions are outlined below.

The liquid chromatogram is presented in Figure 5.

Figure 5: Liquid Chromatogram (Source: QCS R&D Center)
3. Solvent Residues
In accordance with the sample production and treatment procedures, potential residual solvents in the samples were analyzed. The detected solvent residues included methyl isobutyl ketone and isopropylamine. Quantification was performed using the external standard method, and the results are presented in Figure 6.


Figure 6: Chromatogram of Solvent Residue (Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
4. Determination of Incandescent Residue
The incandescent residue of the sample was determined in accordance with General Rule 0841 of Part IV of the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. A precisely weighed quantity of 1.0 g of the test substance was placed in a pre-weighed crucible. The crucible was then placed on an electric hot plate and gradually heated until complete carbonization occurred, followed by cooling. Approximately 1 mL of sulfuric acid was added to moisten the residue, which was subsequently heated at a low temperature until all sulfuric acid fumes were exhausted. The crucible was incinerated at 700 °C until complete ashing was achieved. After transferring the crucible to a desiccator and allowing it to cool, it was reweighed with precision. The crucible was then incinerated again at 700-800 °C until constant weight was reached. The final result indicated that the incandescent residue of the sample was 0.03%, as illustrated in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Drying Weight Loss Measurement Data (Source: QCS R&D Center)
5. Moisture Measurement Procedures
The water content of the sample was determined using Callister coulometry. The results are presented as follows:

6. Sample Test Results
The comprehensive data for the aforementioned test items are as follows: Final Content = (1 - moisture - incandescent residue - residual solvent) * purity * 100%. The content of the current sample, based on this formula, is determined to be 99.45%.
The product test report is presented in Figure 8 below.

Figure 8: Analysis of S-isomer Content in Betalolol
(Source: QCS Research and Development Center)
If you ever need help with packaging, configuration, or content calibration, please don't hesitate to reach out to our sales representative. We're here to assist you!

Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
Join Our Email List
Subscribe to receive updates on new
products, promotions and resources!
| ISO 17034:2016 |
| ISO 9001:2015 |

*All our products are for R&D.

*All our products are for R&D.
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved. 粤ICP备2023004355号
Copyright © 2021-2024 QCSRM All rights reserved.
粤ICP备2023004355号